This is the multi-page printable view of this section.
Click here to print.
Return to the regular view of this page.
Ohlala SmartOps Documentation
Complete documentation for Ohlala SmartOps - AI-powered EC2 management in Microsoft Teams
Ohlala SmartOps is an AI-powered infrastructure management solution that brings AWS EC2 operations directly into Microsoft Teams. Using Amazon Bedrock’s Claude AI, it understands natural language commands and provides intelligent responses with visual dashboards.
Quick Navigation
Core Capabilities
- Conversational AI Interface - Manage infrastructure using plain English
- Intelligent Analysis - On-demand health checks and anomaly detection
- Cost Optimization - Automated rightsizing recommendations
- Remote Troubleshooting - SSM integration for command execution
- Visual Dashboards - On-demand metrics and reports delivered in Teams
- Enterprise Security - Runs in your AWS account with IAM controls
Need Help?
1 - Getting Started with Ohlala SmartOps
Deploy Ohlala SmartOps and begin managing EC2 instances through Microsoft Teams or Google Chat
What You’ll Accomplish
By completing this guide, you’ll be able to:
- Deploy SmartOps in your AWS account
- Connect it to Microsoft Teams, Google Chat, or both
- Execute your first EC2 management commands
- View health reports and cost optimization recommendations
Deployment Steps
The deployment process is organized into clear, manageable steps:
Estimated Time: 15-20 minutes total
Difficulty: Intermediate
Prerequisites: AWS account with admin access, plus either Azure account (for Teams) or Google Workspace (for Google Chat)
Verify you have everything needed before starting
- AWS account requirements
- Microsoft Teams or Google Workspace setup
- Required permissions
Configure AI model access in your AWS account
- Enable Claude Sonnet 4.5 model
- Verify regional availability
- Understand inference profiles
Get Ohlala SmartOps from AWS Marketplace
- Subscribe to the product
- Download CloudFormation template
- Understand pricing
Create and configure your Teams bot
- Create Azure Bot resource
- Generate authentication credentials
- Configure bot settings
Create Google Cloud Project and credentials
- Create GCP project
- Enable Google Chat API
- Generate service account credentials
Launch the infrastructure in AWS
- Configure stack parameters (including chat platform selection)
- Deploy resources
- Monitor deployment progress
Integrate the bot with Microsoft Teams
- Configure webhook URL
- Install Teams app
- Test the connection
Configure the Chat app and install the bot
- Configure Chat app with webhook URL
- Set visibility and permissions
- Install the app
Confirm everything is working
- Run test commands
- Check health reports
- Troubleshoot common issues
Quick Start Links
Pro Tips
- Start Simple: Begin with monitoring features before enabling modifications
- Budget Awareness: SmartOps includes intelligent cost tracking with $5 milestone warnings
- Clear Error Messages: The bot provides actionable guidance when issues occur
- Team Collaboration: Share the assistant with your team for maximum productivity
Need Help?
1.1 - Prerequisites
Check all requirements before deploying Ohlala SmartOps
Ohlala SmartOps supports Microsoft Teams, Google Chat, or both. Choose based on your organization’s needs:
| Platform |
Best For |
Requirements |
| Microsoft Teams |
Organizations using Microsoft 365 |
Azure account, Teams workspace |
| Google Chat |
Organizations using Google Workspace |
Google Cloud project, Workspace account |
| Both |
Organizations using both platforms |
All requirements from both |
Recommendation: If your organization primarily uses one platform, start with that. You can add the second platform later by updating your CloudFormation stack.
AWS Requirements
AWS Account
- Administrative access to create IAM roles, ECS clusters, and other resources
- AWS Marketplace subscription capability
- Billing enabled for AWS services usage
Required AWS Services
Ensure these services are available in your chosen region:
- Amazon ECS Fargate - Container orchestration
- Amazon Bedrock - AI model access
- API Gateway - Teams webhook endpoint
- CloudFormation - Infrastructure deployment
- Systems Manager (SSM) - Instance management
Existing Infrastructure
- At least 1 EC2 instance to manage
- SSM Agent installed on instances
Microsoft Teams Requirements
Skip this section if you plan to use Google Chat only.
Azure Account
- Azure subscription (Free tier works)
- Ability to create resources in Azure Portal
- Azure AD tenant for authentication
Teams Workspace
- Microsoft Teams installed and configured
- Admin permissions to install custom apps
- Teams channel where you want to add the bot
Google Workspace Requirements
Skip this section if you plan to use Microsoft Teams only.
- Google Cloud account with ability to create projects
- Billing enabled (for API usage tracking, minimal cost)
- Permissions to enable APIs and create service accounts
Google Workspace
- Google Workspace account (Business, Enterprise, or Education)
- Admin permissions to create and manage Chat apps, or
- Developer permissions to create internal Chat apps
- Google Chat enabled in your Workspace
Note: Personal Gmail accounts cannot create Chat apps for workspace use. You need a Google Workspace account.
Knowledge Requirements
Recommended Skills
- Basic understanding of AWS services
- Familiarity with CloudFormation
- Experience with your chosen chat platform administration (Teams or Google Chat)
- Understanding of bot concepts
Pre-Deployment Checklist
Use this checklist to verify readiness:
AWS (Required for all)
Microsoft Teams (if using Teams)
Google Chat (if using Google Chat)
Regional Availability
Ohlala SmartOps works in ALL AWS regions through intelligent inference profile selection!
Recommended Regions
For optimal performance, we recommend:
- US East (N. Virginia) - us-east-1
- US West (Oregon) - us-west-2
- Europe (Ireland) - eu-west-1
- Europe (Frankfurt) - eu-central-1
All Supported Regions
The solution works in any region with ECS Fargate support. Bedrock access is automatically handled through cross-region inference profiles.
Next Step
Once you’ve verified all prerequisites:
Continue to Bedrock Setup →
1.2 - Enable Amazon Bedrock
Configure Amazon Bedrock Claude model access for AI capabilities
Important: You MUST enable Amazon Bedrock Claude model access before deployment. Without this, the bot will display an error message guiding you to enable model access.
Why Bedrock is Required
Ohlala SmartOps uses Amazon Bedrock with Claude Sonnet 4.5 to provide:
- Natural language understanding of your commands
- Intelligent analysis of infrastructure issues
- Smart recommendations for optimization
- Context-aware responses based on your environment
Step-by-Step Setup
1. Open Amazon Bedrock Console
Navigate to the Amazon Bedrock console in your deployment region:
Open Amazon Bedrock Console
Important: Open Bedrock in the same region where you plan to deploy Ohlala SmartOps.
2. Navigate to Model Access
In the left sidebar, click on “Model access”
3. Enable Claude Sonnet 4.5
- Click “Modify model access”
- Find and enable:
- Claude Sonnet 4.5 (anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-*)
- Click “Submit” to request access
4. Wait for Approval
- Standard models are usually approved immediately
- Wait for status to show “Access granted”
- Refresh the page if needed
Regional Considerations
How Regional Access Works
Ohlala SmartOps automatically handles regional model access:
- Detects your deployment region
- Uses the optimal inference profile for your location
- No additional configuration needed
- Same performance across all regions
Primary Regions (Native Support)
Best performance in these regions:
- US East (N. Virginia) - us-east-1
- US West (Oregon) - us-west-2
- Europe (Frankfurt) - eu-central-1
- Europe (Ireland) - eu-west-1
- Asia Pacific (Tokyo) - ap-northeast-1
- Asia Pacific (Sydney) - ap-southeast-2
All Other Regions
Supported via cross-region inference profiles:
- Europe (Paris) - eu-west-3
- Europe (London) - eu-west-2
- Asia Pacific (Singapore) - ap-southeast-1
- Asia Pacific (Mumbai) - ap-south-1
- Canada (Central) - ca-central-1
- South America (São Paulo) - sa-east-1
- And more…
Verify Access
Check Model Status
- Return to the Model access page
- Verify Claude Sonnet 4.5 shows “Access granted”
- Note the model ID pattern:
anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-*
Troubleshooting
Model Not Available
- Issue: Claude Sonnet 4.5 not listed
- Solution: Check you’re in a supported region
Access Denied After Deployment
- Issue: Bot shows “Model access required” error
- Solution:
- Enable model access as shown above
- Wait for “Access granted” status
- No need to redeploy - the bot will work automatically
Request Pending Too Long
- Issue: Status stuck on “Pending”
- Solution:
- Cancel and resubmit the request
- Contact AWS Support if issues persist
Good to Know
Model Costs
- Input: $3.00 per million tokens
- Output: $15.00 per million tokens
- Average command uses ~500-2000 tokens
- Built-in cost tracking alerts you at $5 milestones
Alternative Models
Currently, only Claude Sonnet 4.5 is supported. Support for additional models may be added in future releases.
Next Step
Once Bedrock access is enabled:
Continue to AWS Marketplace →
1.3 - AWS Marketplace Subscription
Subscribe to Ohlala SmartOps through AWS Marketplace
What You’ll Get
The AWS Marketplace subscription provides:
- Official CloudFormation template
- Pre-built container images
- Automatic updates
- AWS support integration
- Simplified billing through AWS
Subscription Steps
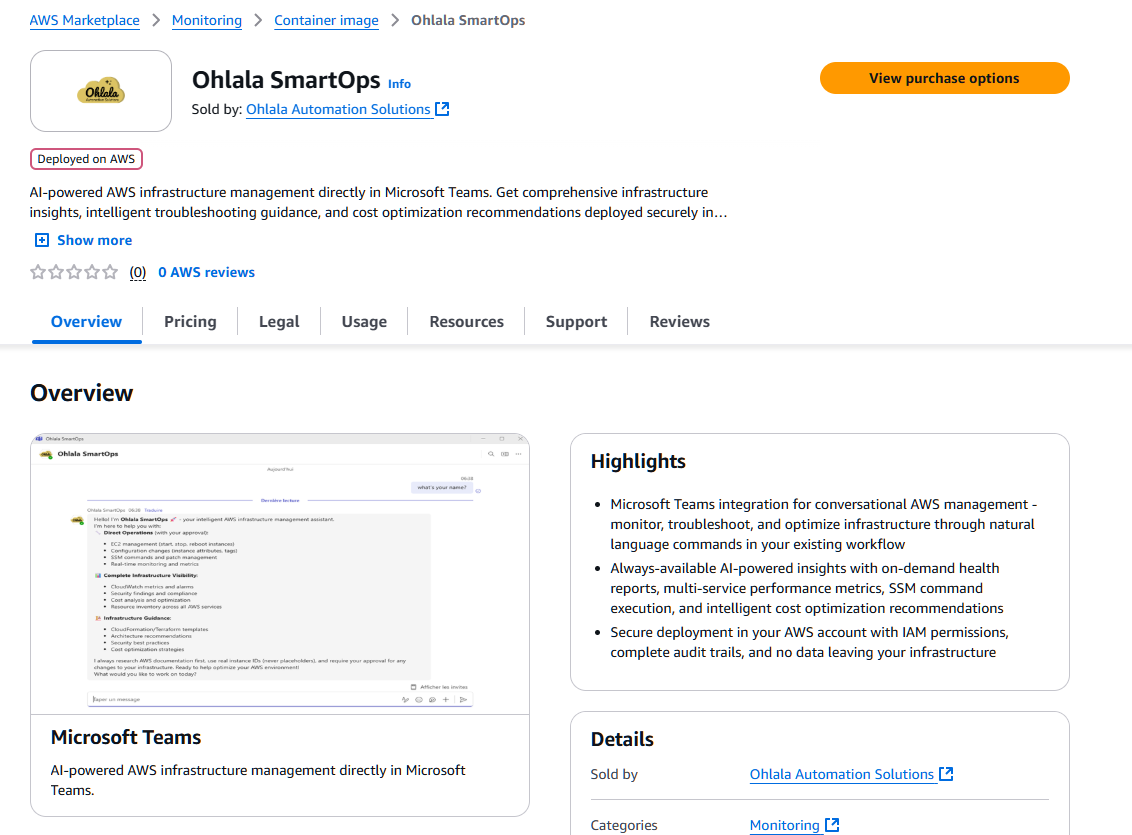
1. Navigate to AWS Marketplace
Open the Ohlala SmartOps product page:
AWS Marketplace - Ohlala SmartOps
2. View Purchase Options
Click “View purchase options” to start the subscription process.
3. Subscribe to the Product
Scroll down and click “Subscribe” to accept the terms.
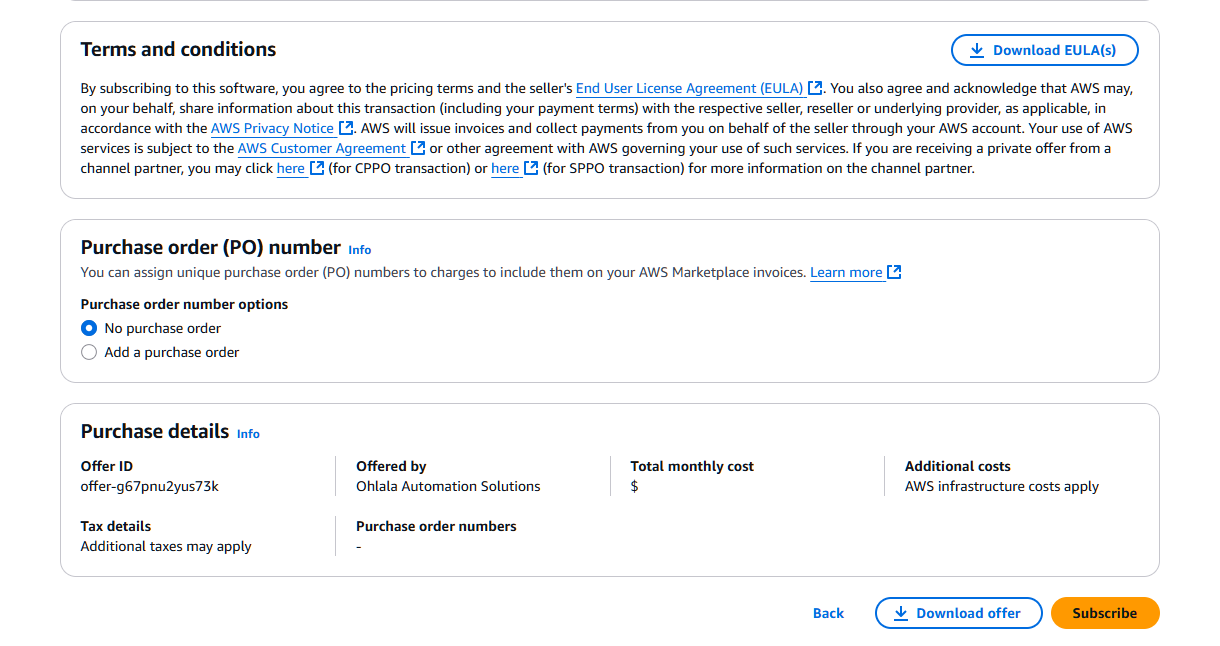
Note: Subscription activation typically takes 1-2 minutes. Wait for the confirmation before proceeding.
4. Launch Your Software
Once subscribed, click “Launch your software” to proceed with deployment.
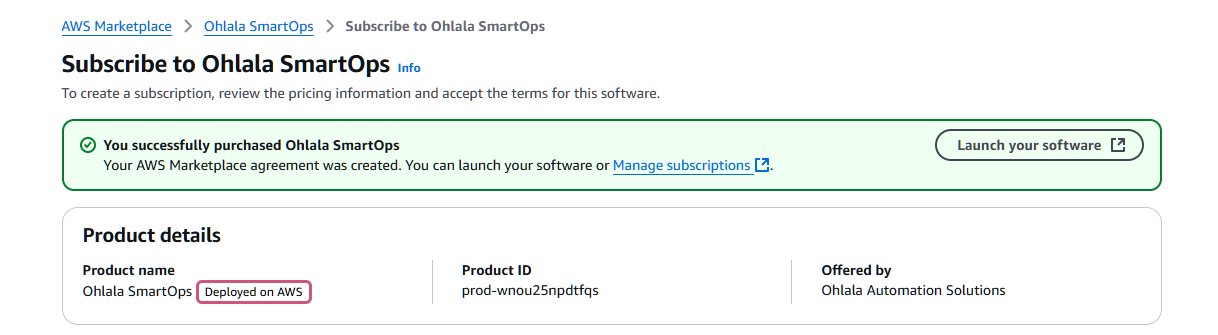
- Select “Amazon ECS” as the launch method
- Click the “cloudformation template” link to download
- Save the template file locally - you’ll need it in the next steps
- Alternatively, you can download the cloudformation template here: Download Template
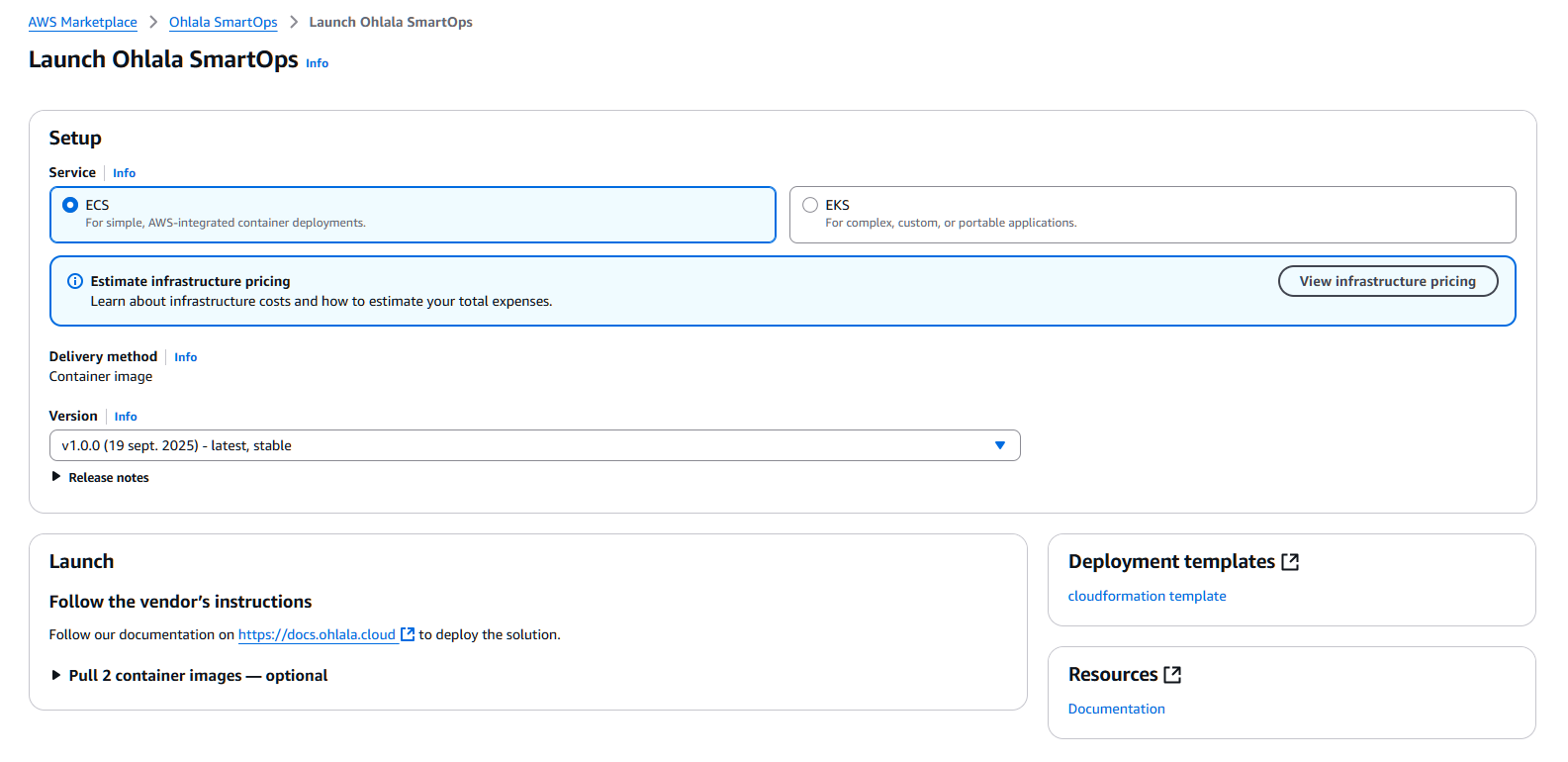
Verify Subscription
Check Subscription Status
- Go to AWS Marketplace → Manage subscriptions
- Find “Ohlala SmartOps” in your subscriptions
- Verify status shows “Active”
Download Template Backup
Important: Save the CloudFormation template file! You’ll need it for deployment.
Common Questions
Q: Can I cancel anytime?
A: Yes, you can cancel the subscription anytime through AWS Marketplace. You only pay for resources used.
Q: Can I deploy multiple instances?
A: Yes, you can deploy multiple stacks using the same subscription. Contact us for volume licensing.
Q: How do updates work?
A: Updates are provided through new versions in Marketplace. You can update at your convenience.
Next Step
With your subscription active and template downloaded:
Continue to Azure Bot Setup →
1.4 - Azure Bot Registration
Create and configure your Microsoft Teams bot in Azure
What You’ll Create
- Azure Bot resource for Teams integration
- Authentication credentials (App ID, Password, Tenant ID)
- Secure communication channel with Teams
Step-by-Step Setup
1. Access Azure Portal
Navigate to Azure Portal and sign in:
https://portal.azure.com
Free Azure Account: If you don’t have an Azure account, you can create one for free with $200 credits.
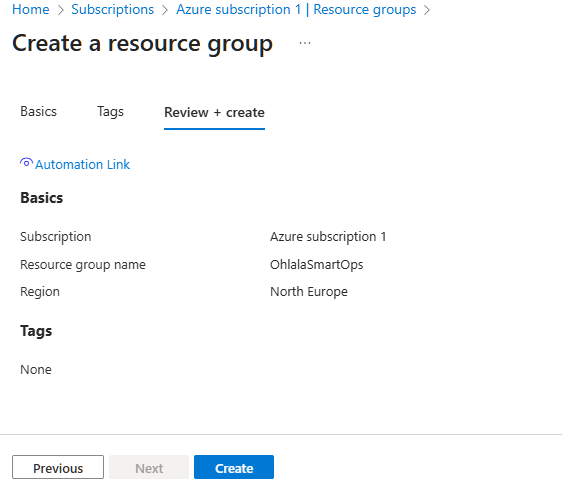
2. Create Resource Group (Optional)
It’s recommended to create a dedicated resource group:
- Search for “Resource groups” in the search bar
- Click “Create”
- Configure:
- Subscription: Your Azure subscription
- Resource group:
ohlala-smartops-rg
- Region: Choose any region (e.g., North Europe)
- Click “Review + create” then “Create”
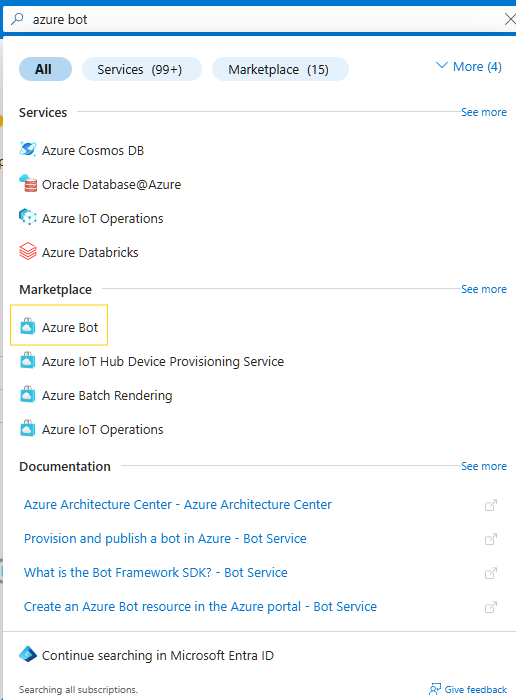
3. Create Azure Bot
Search for Azure Bot
In the Azure Portal search bar, type “Azure Bot” and select it from the marketplace.
Fill in the bot configuration:
Bot handle: OhlalaSmartOps
Subscription: Your Azure subscription
Resource group: ohlala-smartops-rg (or your chosen group)
Location: North Europe (or your preferred region)
Pricing tier: F0 (Free)
Type: Single Tenant (default)
Microsoft App ID: Create new
Bot Handle: Choose a unique name. This won’t be visible to end users.
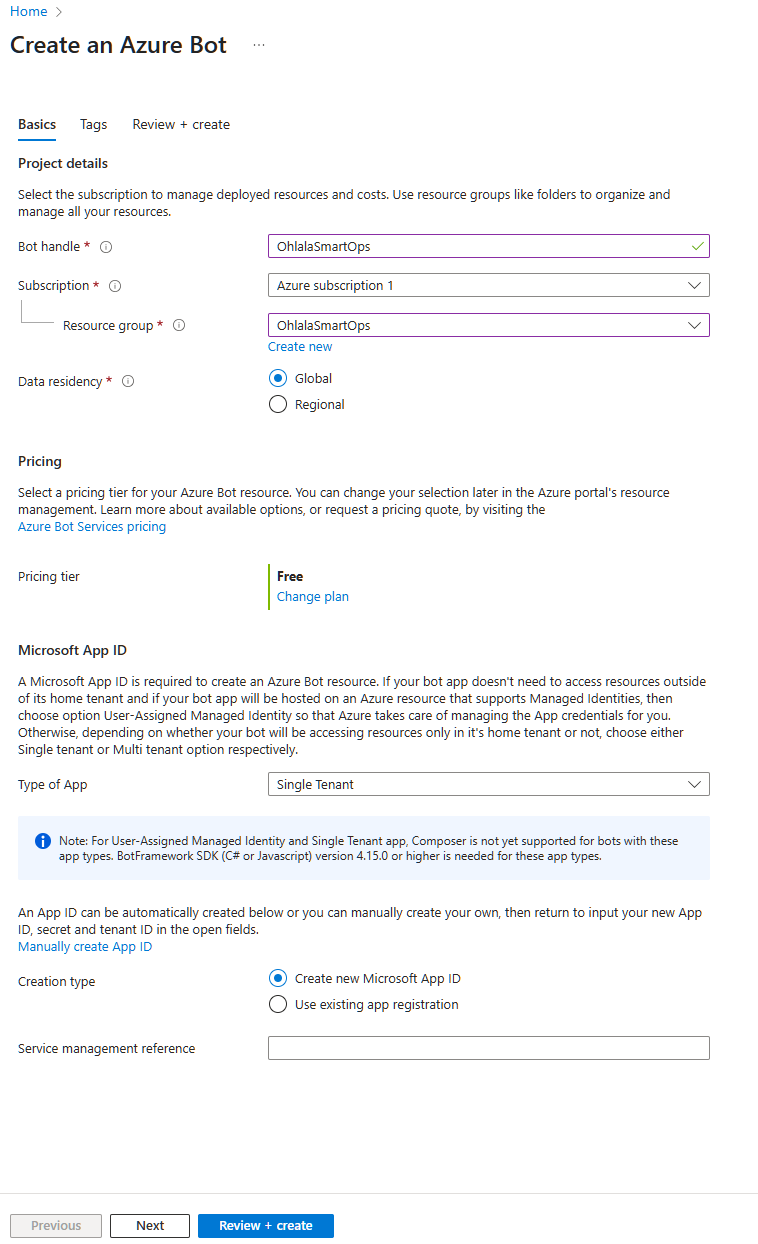
Click “Review + create” then “Create”. Deployment takes about 1-2 minutes.
4. Get Authentication Credentials
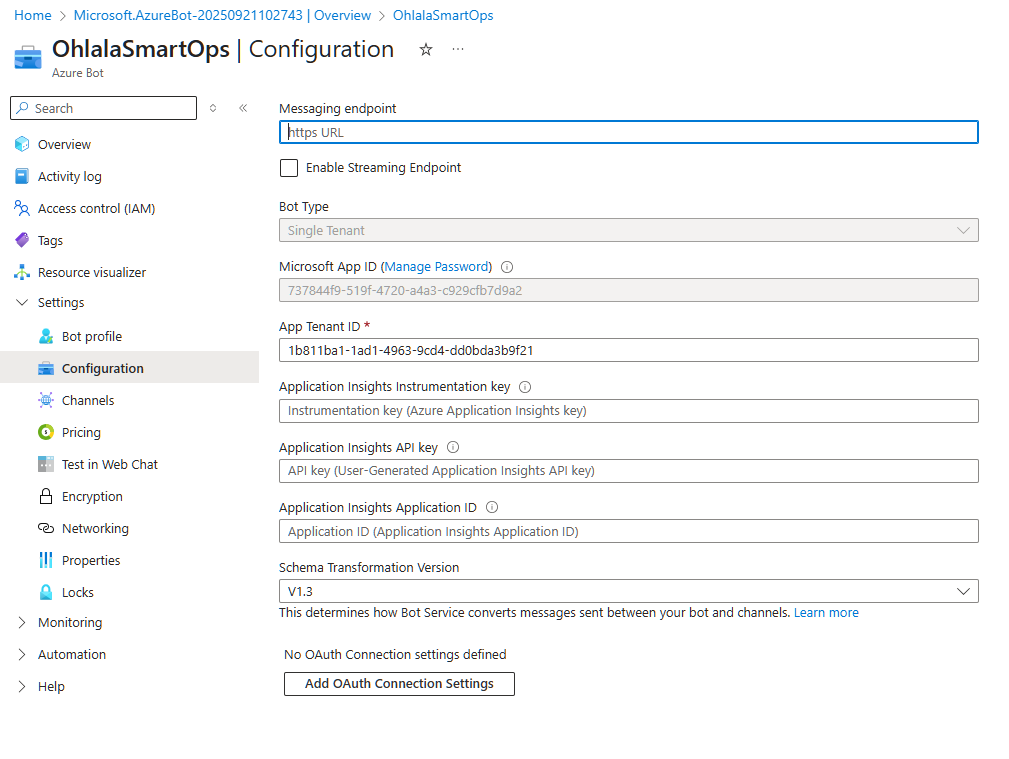
After deployment completes, go to your bot resource.
Navigate to Configuration
- Go to Settings → Configuration
- You’ll see the Microsoft App ID - copy and save this
Create App Password
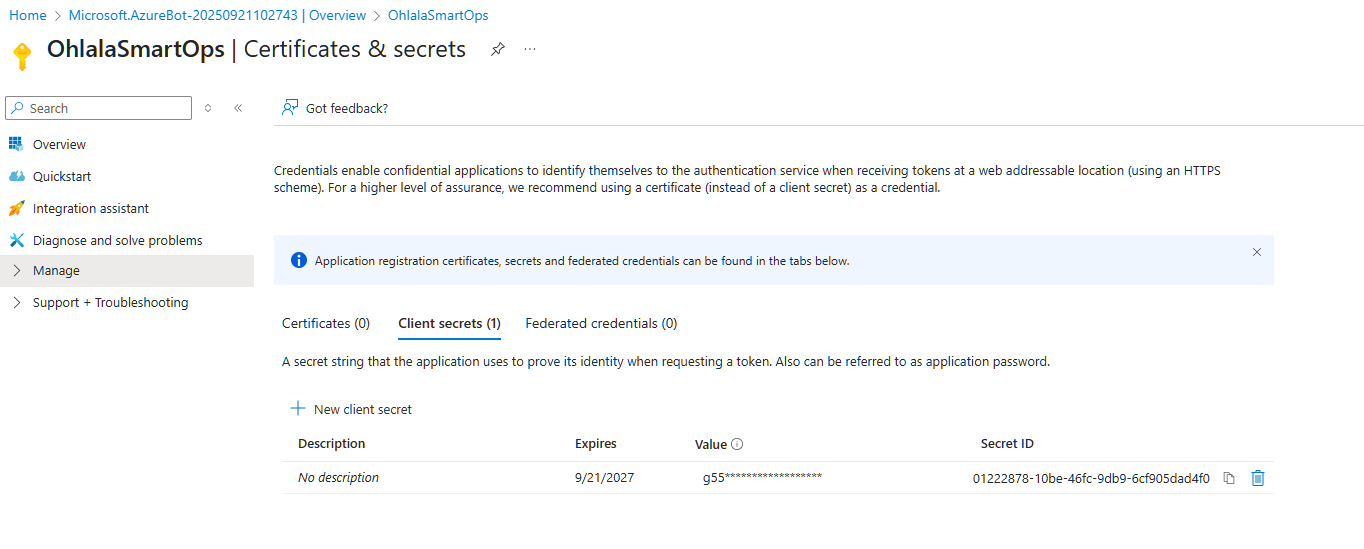
- Click “Manage Password” next to the App ID
- In the new window, click “New client secret”
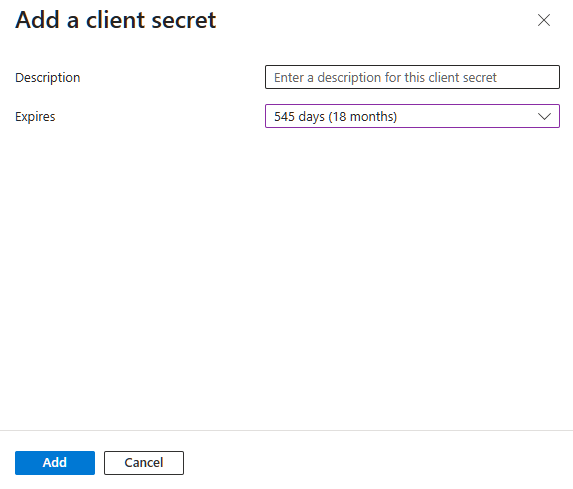
- Configure the secret:
- Description:
Ohlala SmartOps Bot Secret
- Expires: Choose duration (recommend 24 months)
- Click “Add”
- IMPORTANT: Copy the secret value immediately!
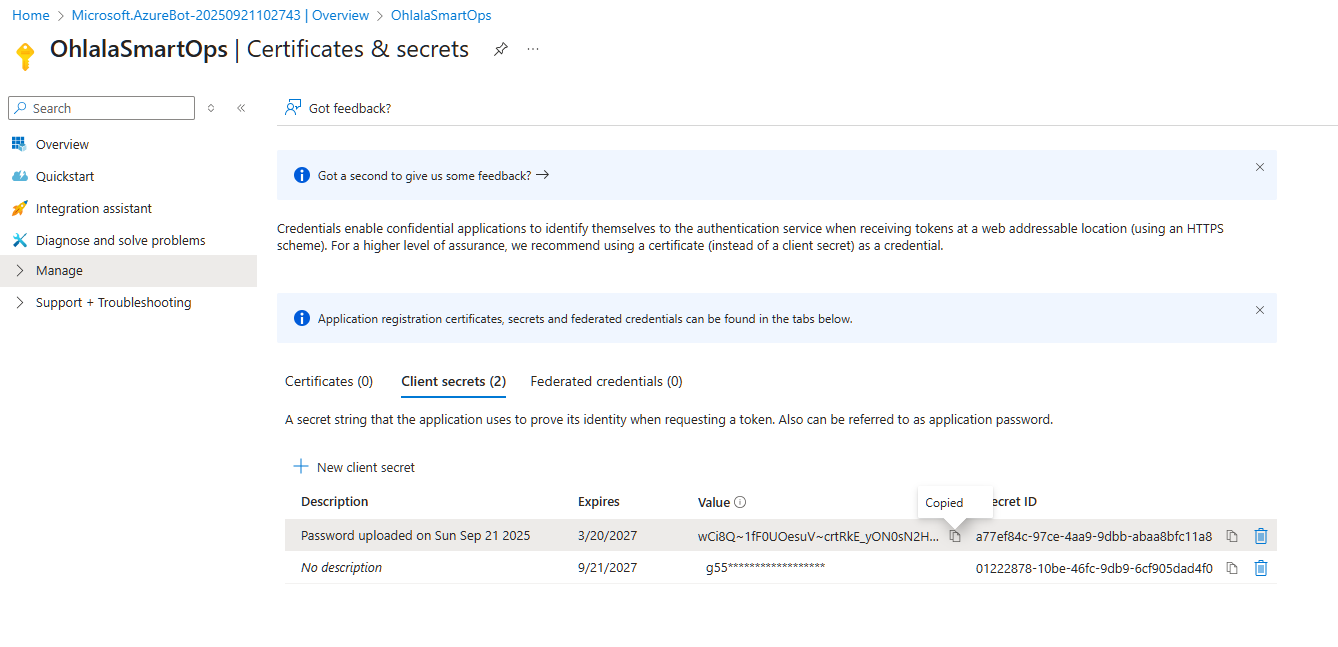
Critical: Save the password now! You cannot view it again after leaving this page.
Get Tenant ID
The Tenant ID is shown in the Azure Portal:
- Click on your account menu (top right)
- Select “Switch directory”
- Your Tenant ID is displayed there
Alternatively:
- Go to Azure Active Directory
- The Tenant ID is on the overview page
Save Your Credentials
You now have three critical values needed for deployment:
| Credential |
Where to Find |
Example |
| Microsoft App ID |
Bot Configuration page |
12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789012 |
| Microsoft App Password |
Client secrets (copied) |
AbC123... (long string) |
| Microsoft App Tenant ID |
Azure AD or account menu |
87654321-4321-4321-4321-210987654321 |
Security Note: Keep these credentials secure. Never commit them to source control or share them publicly.
1. Open Channels Page
In your Azure Bot resource, navigate to Channels in the left sidebar.
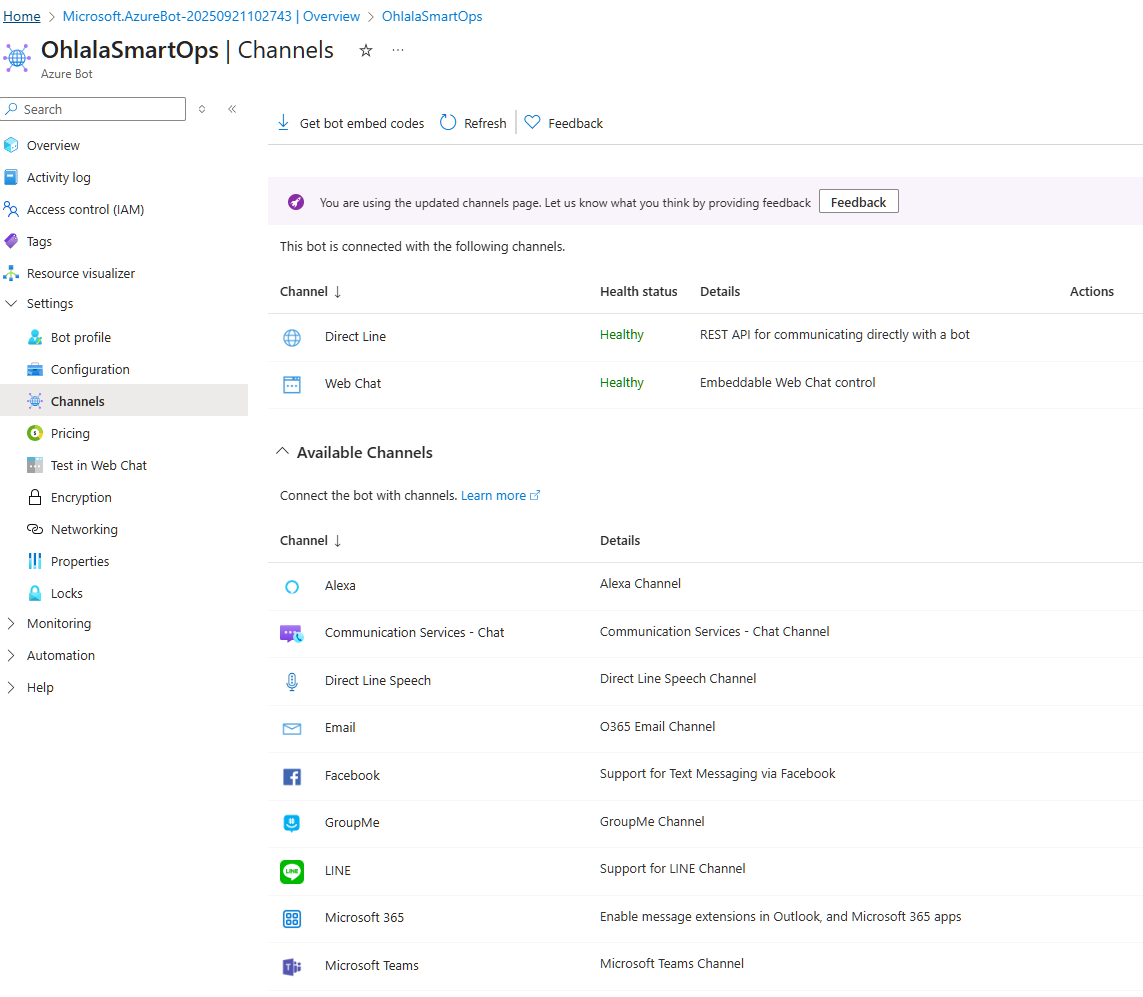
2. Add Microsoft Teams Channel
- Click on the Microsoft Teams icon
- Accept the terms and click “Agree”
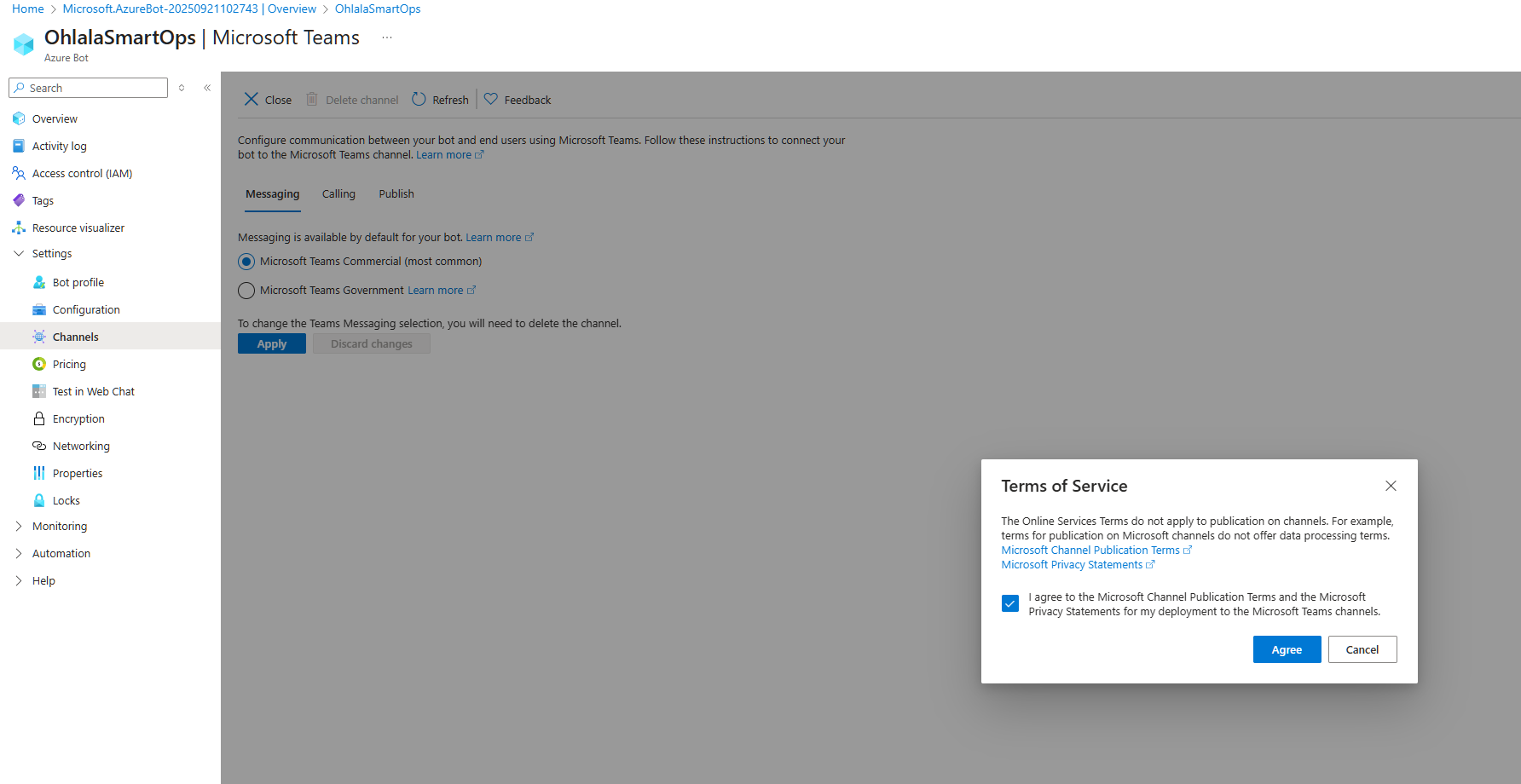
- Click on Apply
Common Issues
Issue: Free Tier Not Available
Solution: F0 tier is limited to one per subscription. Use S1 (Standard) tier instead (~$0.50/month).
Issue: Can’t Create App Password
Solution: You need appropriate permissions in Azure AD. Contact your Azure administrator.
Issue: Lost App Password
Solution: You can create a new client secret:
- Go to Bot Configuration → Manage Password
- Create a new client secret
- Update your deployment with the new password
Next Step
With your Azure Bot configured and credentials saved:
Continue to CloudFormation Deployment →
1.5 - Google Cloud Setup
Create Google Cloud Project and Service Account for Google Chat integration
Platform Selection: This section is for users who will select
GoogleChat or
Both as their ChatPlatform. Teams-only users: skip to
CloudFormation Deployment.
What You’ll Create
- Google Cloud Project
- Service Account with JSON credentials
- Enabled Google Chat API
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
- Google Cloud Platform account with billing enabled
- Google Workspace account (Business, Enterprise, or Education)
Step-by-Step Setup
1. Create Google Cloud Project
Set Up Project
- Go to Google Cloud Console
- Click Select a project then New Project

-
Enter project name: ohlala-smartops (or your preferred name)
-
Click Create

-
Wait for project creation to complete
Important: Note your Project ID (shown below project name). You’ll need this for CloudFormation parameters.
2. Enable Google Chat API
-
In Google Cloud Console, go to APIs & Services then Library
-
Search for Google Chat API

-
Click Google Chat API
-
Click Enable

3. Create Service Account
Create the Account
- Go to IAM & Admin then Service Accounts
- Click Create Service Account

- Enter details:
- Name:
ohlala-smartops-bot
- ID:
ohlala-smartops-bot (auto-generated)
- Description:
Service account for Ohlala SmartOps Chat app

- Click Create and Continue
- Skip the optional steps (roles, access)
- Click Done
Generate JSON Key
- Click on your new service account
- Go to Keys tab
- Click Add Key then Create new key

- Select JSON format
- Click Create
- Save the downloaded JSON file securely

Security: Keep this JSON file secure. It contains credentials that grant access to your Chat app. Never commit it to version control.
You’ll need two values for CloudFormation deployment:
| Credential |
CloudFormation Parameter |
Where to Find |
| Project ID |
GoogleChatProjectId |
Visible in Google Cloud Console (top bar or project settings) |
| Service Account JSON |
GoogleChatServiceAccountInfo |
Downloaded JSON file (converted to single line) |
Convert JSON to Single Line
The service account JSON must be on a single line for CloudFormation. Use one of these methods:
Linux/Mac:
cat service-account.json | jq -c
Windows (PowerShell):
Get-Content service-account.json | ConvertFrom-Json | ConvertTo-Json -Compress
Tip: Copy the output and paste it directly into the CloudFormation GoogleChatServiceAccountInfo parameter.
Summary
At this point, you should have:
Next Step
You’re ready to deploy the CloudFormation stack with your Google Chat credentials:
Continue to CloudFormation Deployment →
1.6 - Deploy CloudFormation Stack
Deploy the Ohlala SmartOps infrastructure in AWS
What Gets Deployed
The CloudFormation stack creates:
- ECS Fargate cluster with container services
- API Gateway for Teams and/or Google Chat webhooks
- Network infrastructure (VPC, subnets, security groups)
- IAM roles with appropriate permissions
- Secrets Manager for credentials
- CloudWatch logs for monitoring
Deployment Steps
Navigate to CloudFormation in your target region:
https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation/home
Important: Choose the same region where your EC2 instances are located and where you enabled Bedrock.
2. Create New Stack
Click “Create stack” and choose “With new resources (standard)”
3. Upload Template
- Select “Choose an existing template”
- Select “Upload a template file”
- Click “Choose file” and select the template downloaded from AWS Marketplace
- Click “Next”
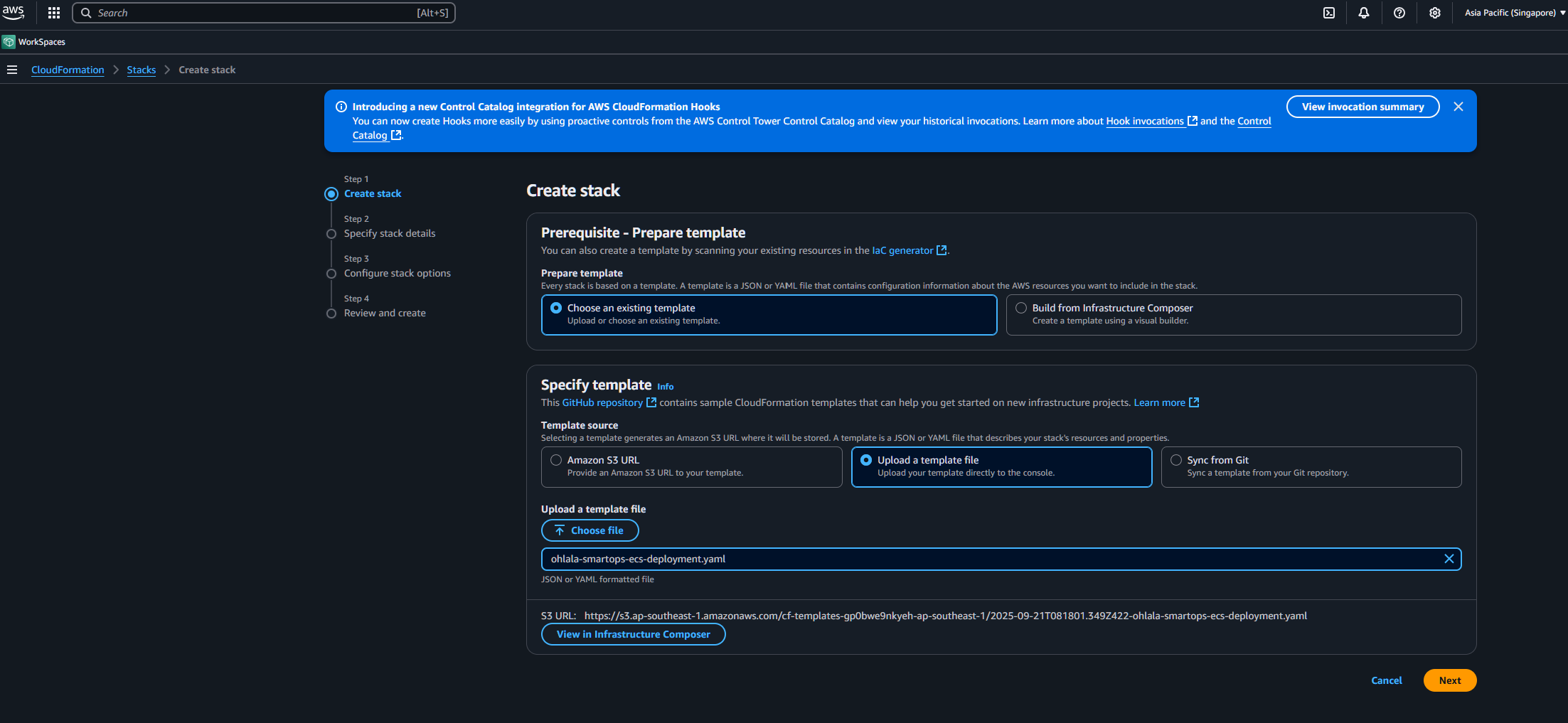
Stack Name
Enter a unique stack name: OhlalaSmartOps (or your preference)
Stack Name: Used to identify resources. Can be anything, but keep it short and memorable.
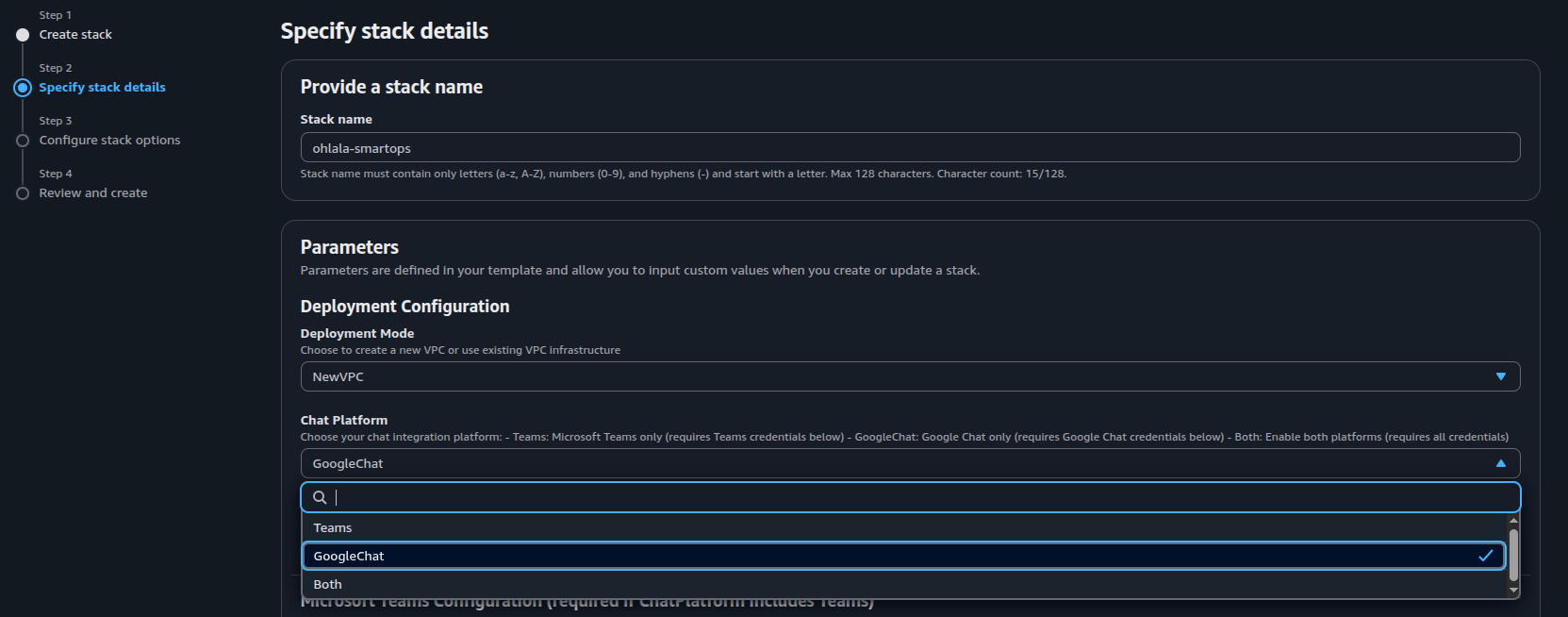
Required Parameters
Fill in the mandatory parameters:
| Parameter |
Description |
Example/Value |
| DeploymentMode |
VPC configuration |
NewVPC (recommended) |
| ContainerImageTag |
Version to deploy |
v2.0.2 (default) |
| ChatPlatform |
Chat integration to enable |
Teams, GoogleChat, or Both |
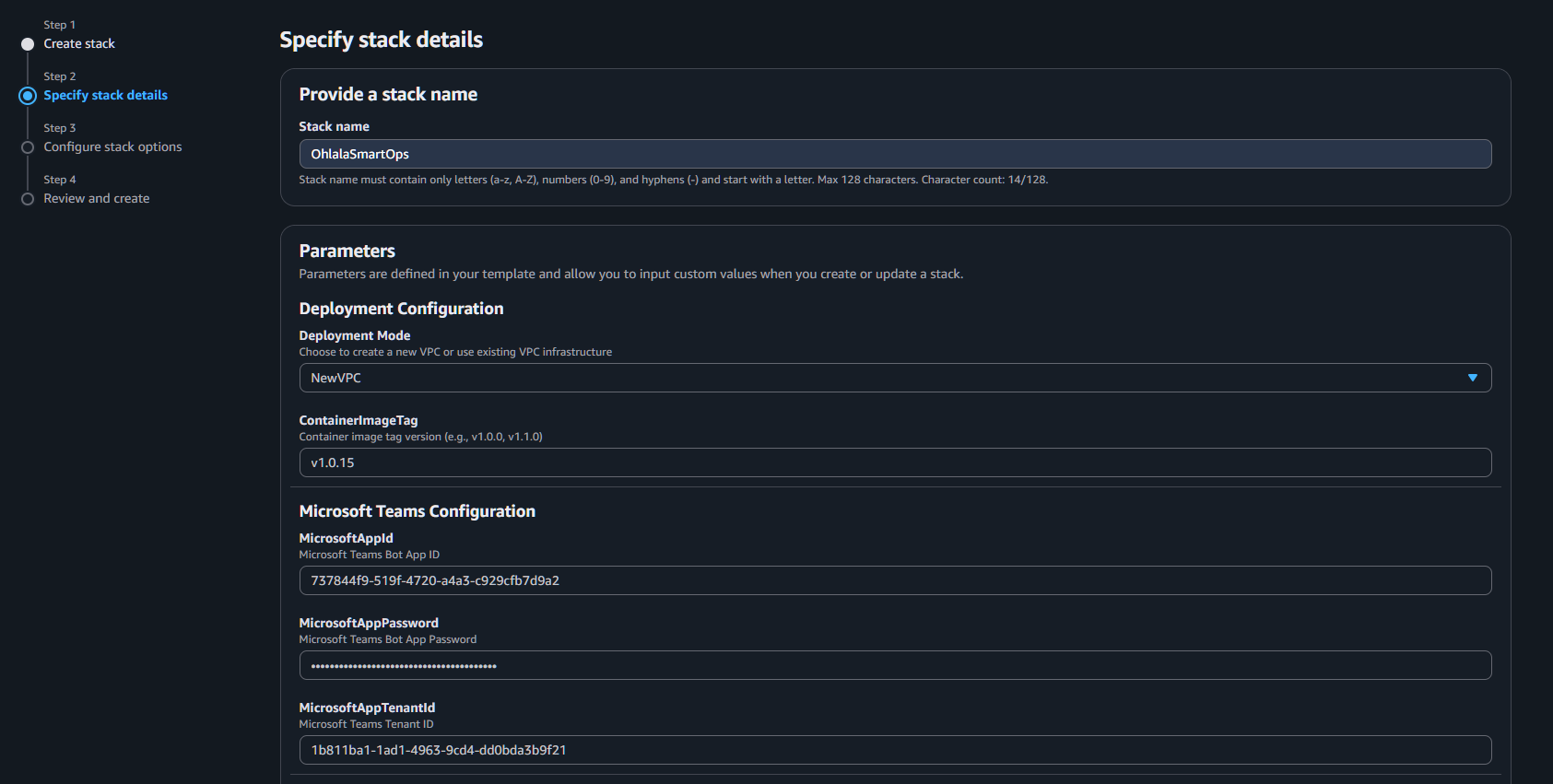
| Parameter |
Description |
Example/Value |
| MicrosoftAppId |
From Azure Bot setup |
Your App ID |
| MicrosoftAppPassword |
From Azure Bot setup |
Your App Password |
| MicrosoftAppTenantId |
From Azure Bot setup |
Your Tenant ID |
Note: Skip the Teams parameters if you selected GoogleChat as your ChatPlatform.
| Parameter |
Description |
Example/Value |
| GoogleChatProjectId |
Your GCP project ID |
my-project-123456 |
| GoogleChatServiceAccountInfo |
Service account JSON key (single line) |
{"type":"service_account",...} |
Note: Skip the Google Chat parameters if you selected
Teams as your ChatPlatform. If you haven’t created your Google Cloud credentials yet, complete
Google Cloud Setup first.
VPC Configuration (if NewVPC)
Keep defaults or customize:
- VPCCIDR:
10.0.0.0/16
- PublicSubnet1CIDR:
10.0.1.0/24
- PublicSubnet2CIDR:
10.0.2.0/24
- PrivateSubnet1CIDR:
10.0.10.0/24
- PrivateSubnet2CIDR:
10.0.11.0/24
- EnableNATGateway:
true
Security & Reports Configuration
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| AllowedIngressCIDR |
CIDR range allowed to access API Gateway |
0.0.0.0/0 |
| EnableDailyReports |
Enable daily health reports to chat platforms |
true |
| DailyReportSchedule |
Cron expression for report schedule |
cron(0 8 * * ? *) |
Daily Reports: When enabled, health reports are sent to all configured chat platforms (Teams and/or Google Chat) at the scheduled time. Reports include EC2 health metrics, software versions, and available patches.
Schedule Examples:
cron(0 8 * * ? *) - Every day at 8am UTCcron(0 9 ? * MON-FRI *) - Weekdays at 9am UTCcron(0 14 * * ? *) - Every day at 2pm UTC
AllowedIngressCIDR: The default 0.0.0.0/0 is recommended because Microsoft Teams Bot Framework uses dynamic Azure IPs globally. Security is enforced by JWT token validation in the Lambda Authorizer, not IP filtering. Only change this if you have specific corporate network restrictions.
Click “Next”
On the stack options page:
- Tags: (Optional) Add tags for resource organization
- Permissions: Leave default
- Advanced options: Leave default
Click “Next”
6. Review and Create
- Review all settings
- Check the acknowledgment box:
- I acknowledge that AWS CloudFormation might create IAM resources with custom names
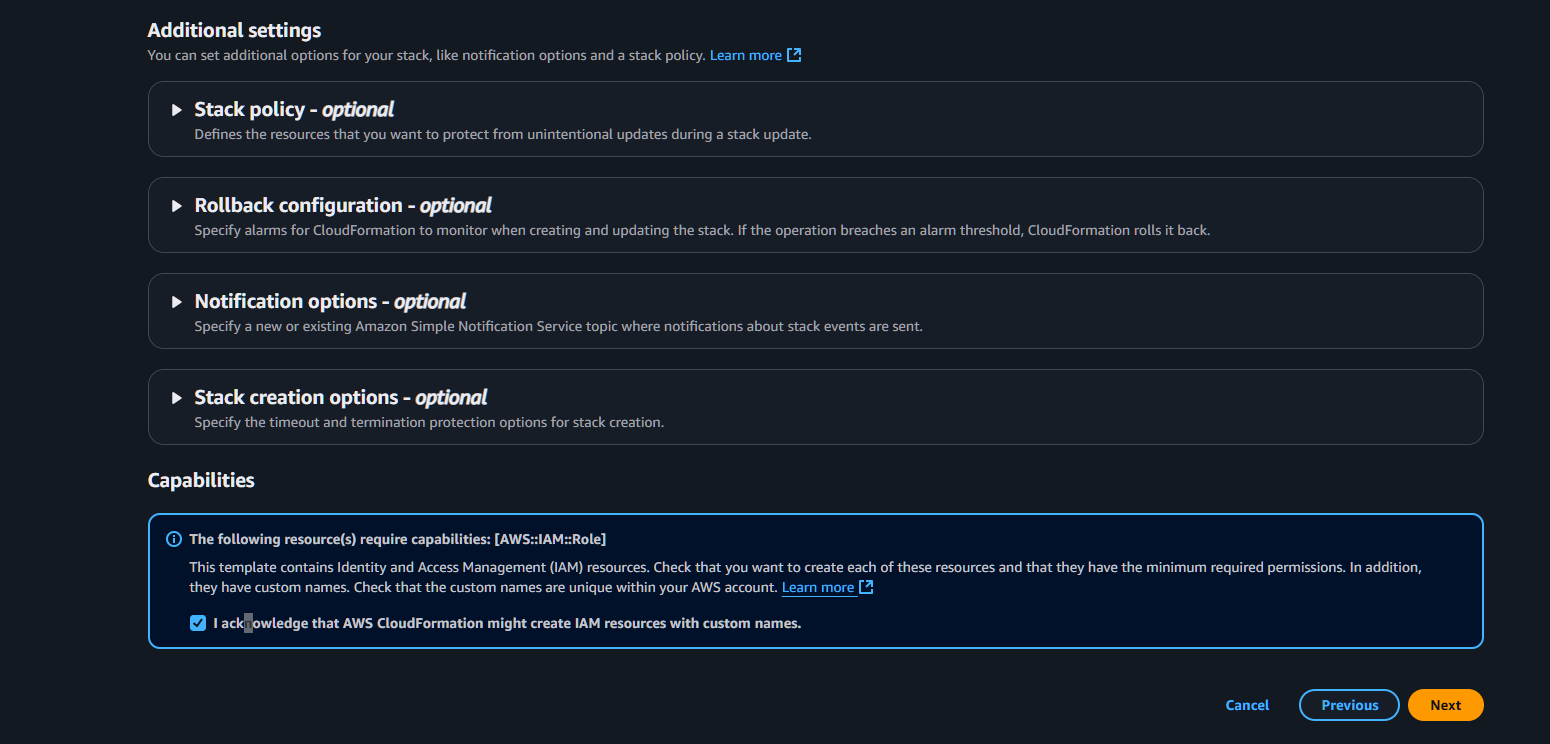
- Click “Submit”
7. Monitor Deployment
The stack creation takes 5-10 minutes. Monitor progress:
- Select your stack in the CloudFormation console
- Check the Events tab for real-time updates
- Wait for status: CREATE_COMPLETE
Success Indicators:
- Stack status shows
CREATE_COMPLETE
- All resources in the Resources tab show
CREATE_COMPLETE
- No errors in the Events tab
Get Stack Outputs
Once deployment completes, get the important URLs:
- Select your stack
- Go to the Outputs tab
- Save these values:
| Output |
Description |
Use |
| TeamsWebhookURL |
API Gateway endpoint for Teams |
Configure in Azure Bot |
| GoogleChatWebhookURL |
API Gateway endpoint for Google Chat |
Configure in Google Chat API |
| APIGatewayEndpoint |
Base API URL |
Reference only |
| ECSCluster |
Cluster name |
For monitoring |
| ECSService |
Service name |
For monitoring |
Note: You will only see the webhook URL outputs relevant to your selected ChatPlatform.
Verify Deployment
Check ECS Service
- Go to ECS Console → Clusters
- Find your cluster (e.g.,
OhlalaSmartOps-Cluster-...)
- Check service shows 1 running task
Check API Gateway
- Go to API Gateway Console
- Find your API (e.g.,
OhlalaSmartOps-API-...)
- Verify endpoints are created
Check Health Endpoint
Test the health endpoint (no authentication required):
curl https://your-api-id.execute-api.region.amazonaws.com/prod-stackname/health
Should return: {"status": "healthy"}
Troubleshooting
Stack Creation Failed
IAM Role Already Exists
Error: “Resource of type ‘AWS::IAM::Role’ with identifier already exists”
Solution: Use a different stack name, or delete the existing role first
Insufficient Permissions
Error: “User is not authorized to perform: iam:CreateRole”
Solution: Ensure you have admin permissions or required IAM policies
Service Quota Exceeded
Error: “Service quota exceeded”
Solution: Request quota increase or deploy in different region
Stack Stuck in CREATE_IN_PROGRESS
- Check Events tab for specific resource causing delay
- ECS service can take 3-5 minutes to stabilize
- If stuck >15 minutes, consider deleting and retrying
Next Step
With infrastructure deployed and webhook URL ready, continue based on your ChatPlatform selection:
1.7 - Connect to Microsoft Teams
Configure the webhook and install the bot in Microsoft Teams
Platform Selection: This section is for users who selected
Teams or
Both as their ChatPlatform in CloudFormation. If you selected
GoogleChat only, proceed to
Google Chat Integration.
- Azure Bot webhook endpoint
- Teams channel connection
- Bot app installation
- Initial testing
Integration Steps
Get the Webhook URL
From your CloudFormation stack outputs, copy the TeamsWebhookURL:
https://xxx.execute-api.region.amazonaws.com/prod-stackname/api/messages
Update Bot Configuration
- Go to Azure Portal
- Navigate to your Azure Bot resource
- Go to Configuration under Settings
- Set Messaging endpoint to your webhook URL
- Click Apply to save
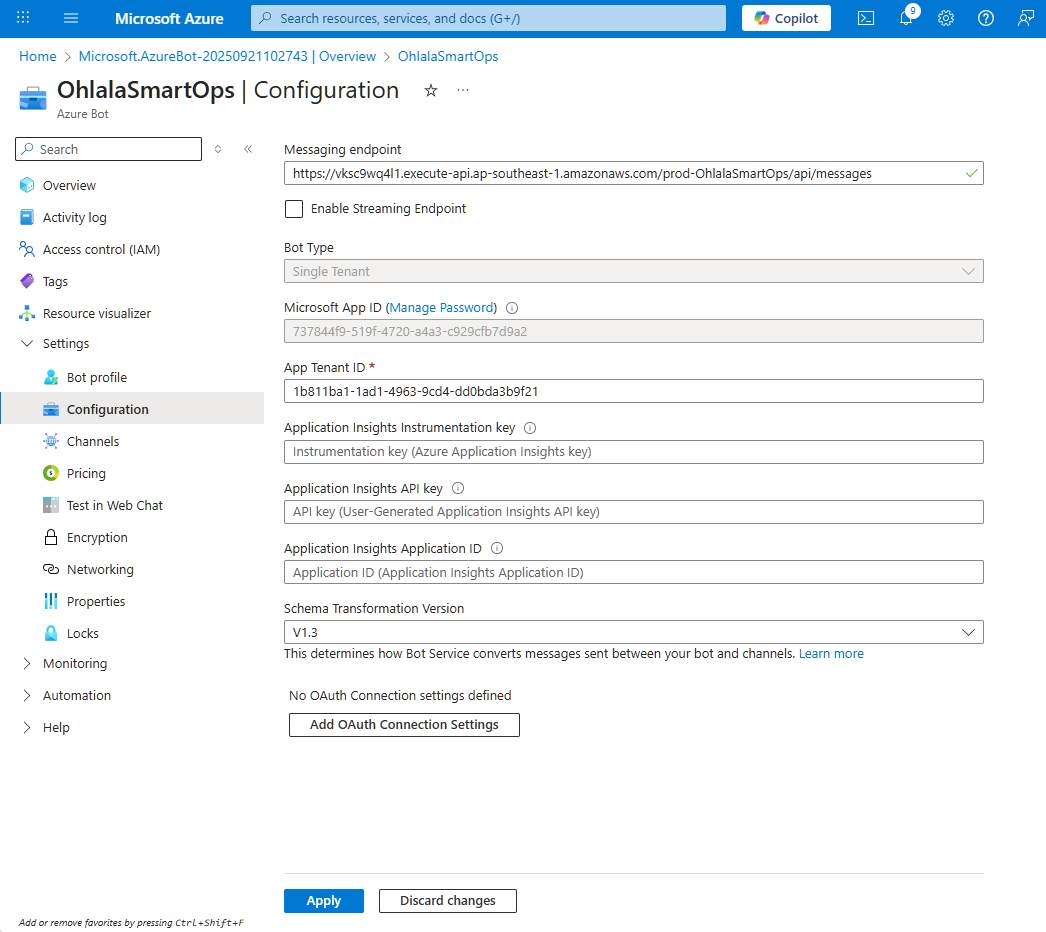
Important: The URL must be exactly as shown in CloudFormation outputs, including /api/messages
2. Install Teams App
-
Download the Teams app package:
Ohlala SmartOps Teams App
-
Customize the manifest:
- Extract the zip file
- Edit
manifest.json
- Replace
YOUR_APP_ID with your Microsoft App ID
- Re-zip the files
-
Install in Teams:
- Open Microsoft Teams
- Go to Apps in the left sidebar, then Manage your apps
- Click Upload an app
- Select Upload a custom app
- Choose your zip file
- Click Add to install


N.B.: You can also ask your Teams admin to upload the app for you if you lack permissions on Teams Admin portal
4. Add Bot to Team or Chat
For Personal Use
- Find Ohlala SmartOps in your apps
- Click Add
- Start chatting directly with the bot
For Team Use
- Go to your team
- Click ⋮ (More options) → Manage team
- Go to Apps tab
- Click Upload a custom app
- Select your app
- Click Add to team
Permissions: Team owners can add apps. Members may need approval depending on your Teams settings.
Test the Connection
Send Test Message
In Teams, message the bot:
@Ohlala SmartOps hello
Expected response:
Hello! I’m Ohlala SmartOps, your AI-powered AWS infrastructure assistant.
Type ‘/help’ to see what I can do for you.
Test Basic Command
Try a simple command:
@Ohlala SmartOps /help
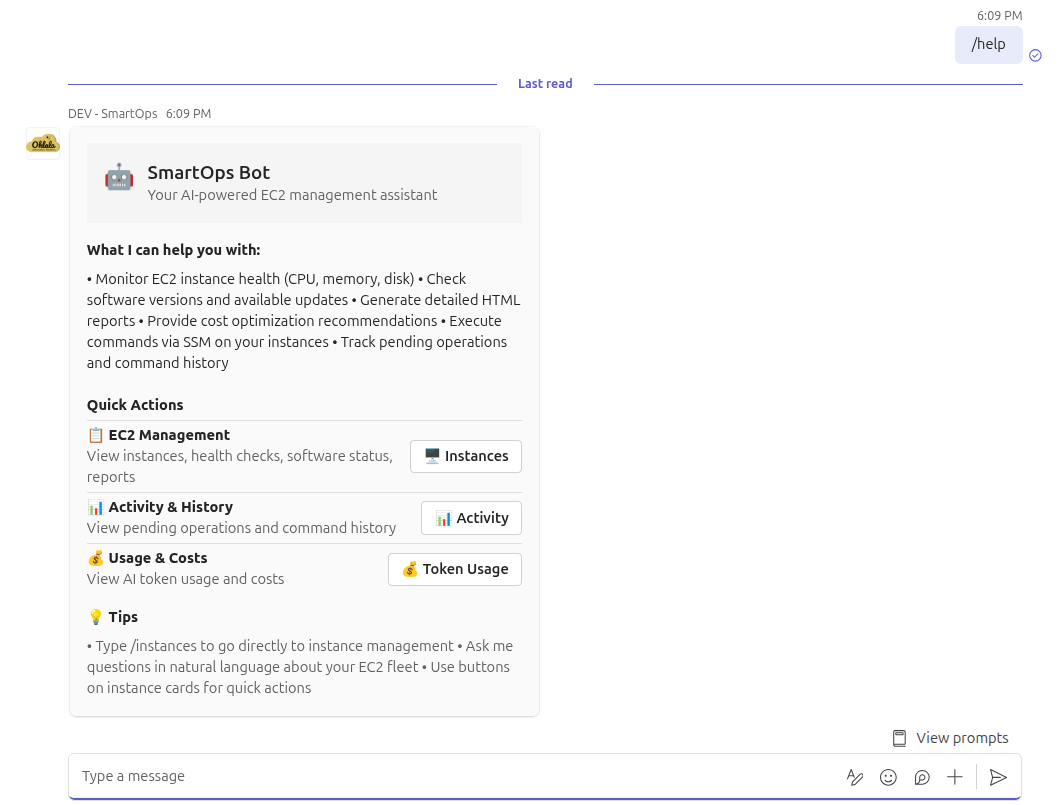
The bot should respond with a help card showing available commands.
Verify Integration
Check Connection Status
In Azure Portal
- Go to your bot → Channels
- Microsoft Teams should show Running
- Click Microsoft Teams to see activity
In AWS Console
- Go to CloudWatch → Log Groups
- Find
/aws/ecs/ohlala-smartops-...
- Check for incoming request logs
Monitor API Gateway
- Go to API Gateway Console
- Select your API
- Go to Dashboard
- You should see incoming requests when messaging the bot
Troubleshooting
Bot Not Responding
Check Webhook URL
- Verify URL in Azure Bot Configuration matches CloudFormation output exactly
- Ensure it includes the full path with
/api/messages
Check ECS Service
- Go to ECS Console
- Verify service has 1 running task
- Check task logs for errors
Test Health Endpoint
curl https://your-api.execute-api.region.amazonaws.com/prod-stackname/health
“Service Unavailable” Error
Causes:
- ECS task not running
- API Gateway misconfigured
- Authentication failing
Solution:
- Check ECS service is running
- Verify API Gateway deployment
- Check CloudWatch logs for details
Authentication Errors
Symptoms: 401 or 403 errors in logs
Solution:
- Verify Microsoft App credentials in Secrets Manager
- Ensure Tenant ID is correct
- Check Lambda authorizer logs
Teams App Installation Issues
“App not found”:
- Ensure manifest.json has correct App ID
- Verify bot is published in Azure
“Permissions required”:
- Contact Teams admin to allow custom apps
- Check organizational app policies
Success Checklist
Confirm everything is working:
Next Step
Your bot is connected! Now let’s verify everything and run your first commands:
Continue to Verification & Testing →
1.8 - Connect to Google Chat
Configure the Chat app and install the bot in Google Chat
Platform Selection: This section is for users who selected
GoogleChat or
Both as their ChatPlatform in CloudFormation. If you selected
Teams only, proceed to
Verification & Testing.
- Chat app settings with webhook URL
- App visibility and permissions
- Bot installation in Google Chat
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
- Google Cloud Project created with Chat API enabled (Google Cloud Setup)
- CloudFormation stack deployed with ChatPlatform set to
GoogleChat or Both
- GoogleChatWebhookURL from CloudFormation stack outputs
Integration Steps
1. Get the Webhook URL
- Go to AWS CloudFormation Console
- Select your stack
- Go to the Outputs tab
- Copy the GoogleChatWebhookURL value
The URL looks like:
https://xxx.execute-api.region.amazonaws.com/prod-stackname/api/google-chat
Access Chat API Configuration
- Go to Google Chat API Configuration
- Or navigate: APIs & Services then Enabled APIs then Google Chat API then Configuration
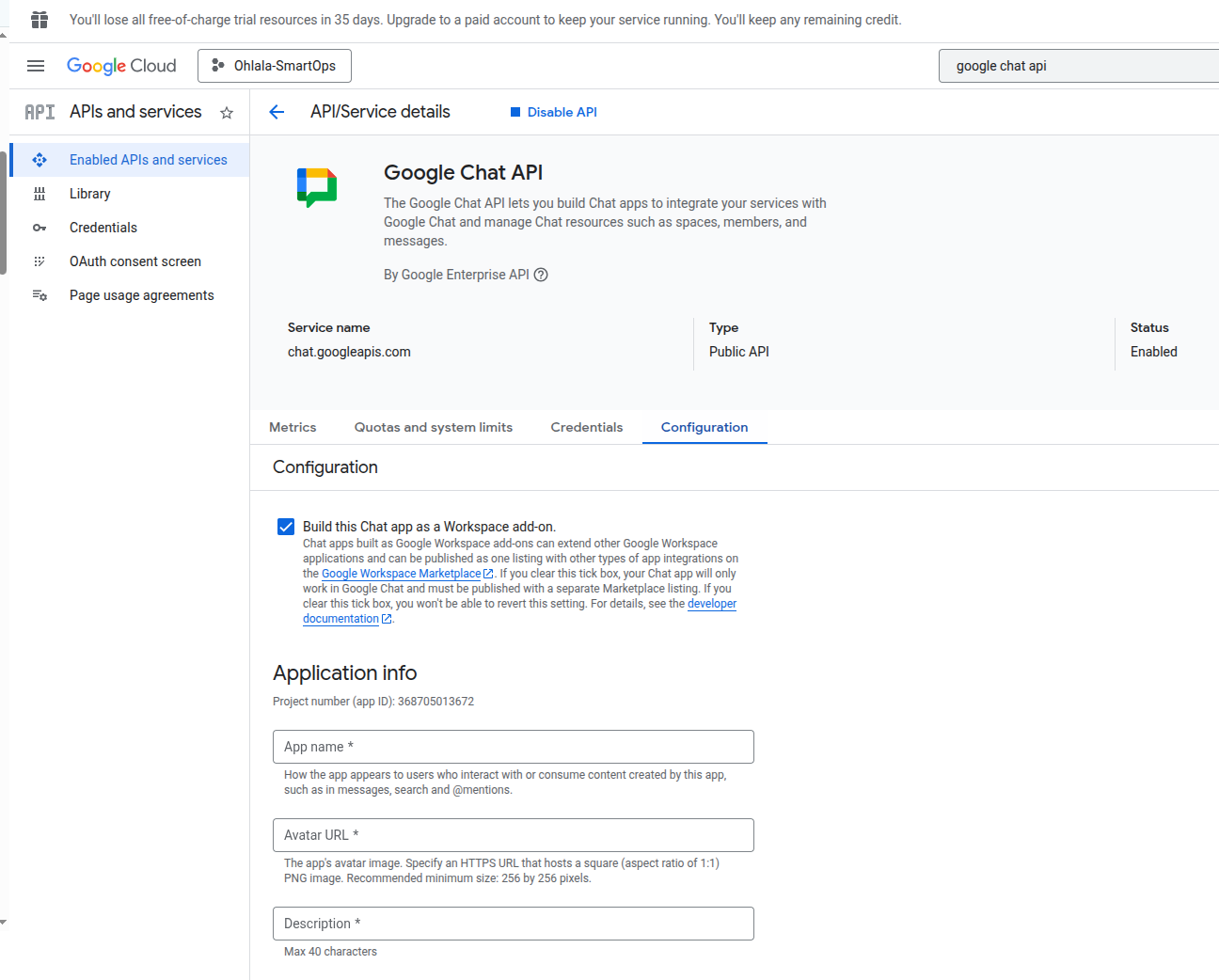
App name: Ohlala SmartOps
Avatar URL: https://767397776277-marketplace.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/Ohlala_logo.png
Description: AI-powered AWS infrastructure management assistant
Enable Interactive features: ON
Functionality: Select both:
- Receive 1:1 messages
- Join spaces and group conversations
Connection settings:
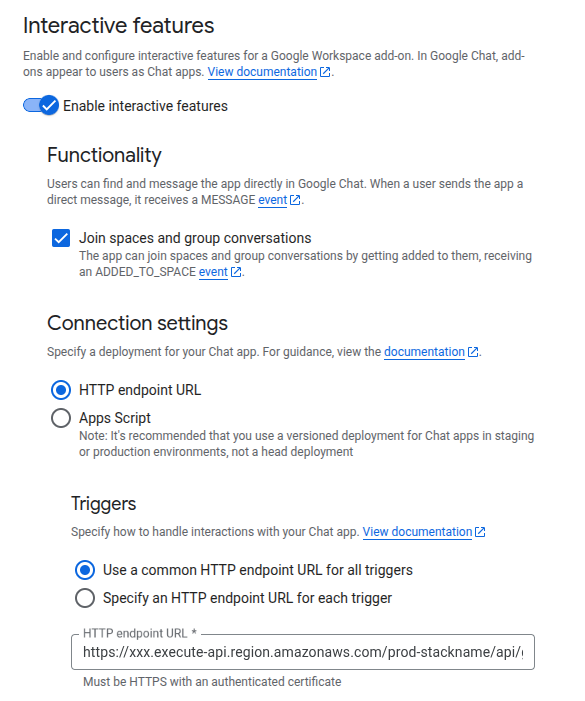
Authentication Audience: Select App URL
Set Visibility
Important: Apps not published through Google Workspace Marketplace must explicitly list allowed users. The app will only appear in “Find apps” for users added here.
- Select “Make this Chat app available to specific people and groups”
- Click Add people or groups
- Enter email addresses of all users who need access to the bot
- Click Save
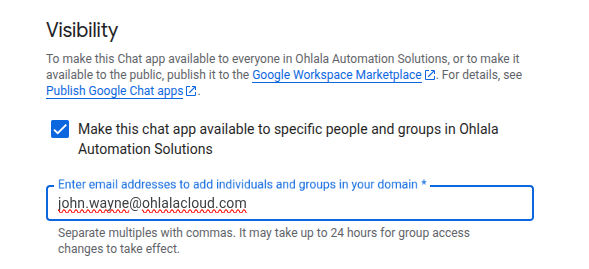
Tip: You can add Google Groups to grant access to multiple users at once.
3. Add Bot to Google Chat
For Personal Use (Direct Message)
- Open Google Chat
- Click + New chat then type “smartops”
- Search for Ohlala SmartOps
- Click on the app
- Click Add
- Start chatting directly with the bot
For Space Use (Group)
- Open or create a Google Chat space
- Click the space name then Integrations
- Click Add apps
- Search for Ohlala SmartOps
- Click Add
- The bot will appear in the space
Visibility Note: The app will only appear in search if you’re included in the visibility settings configured in step 2.
Test the Connection
Send Test Message
In Google Chat, message the bot:
@Ohlala SmartOps hello
Or in a direct message:
hello
Expected response:
Hello! I’m Ohlala SmartOps, your AI-powered AWS infrastructure assistant.
Type ‘/help’ to see what I can do for you.
Test Basic Command
Try a simple command:
/help
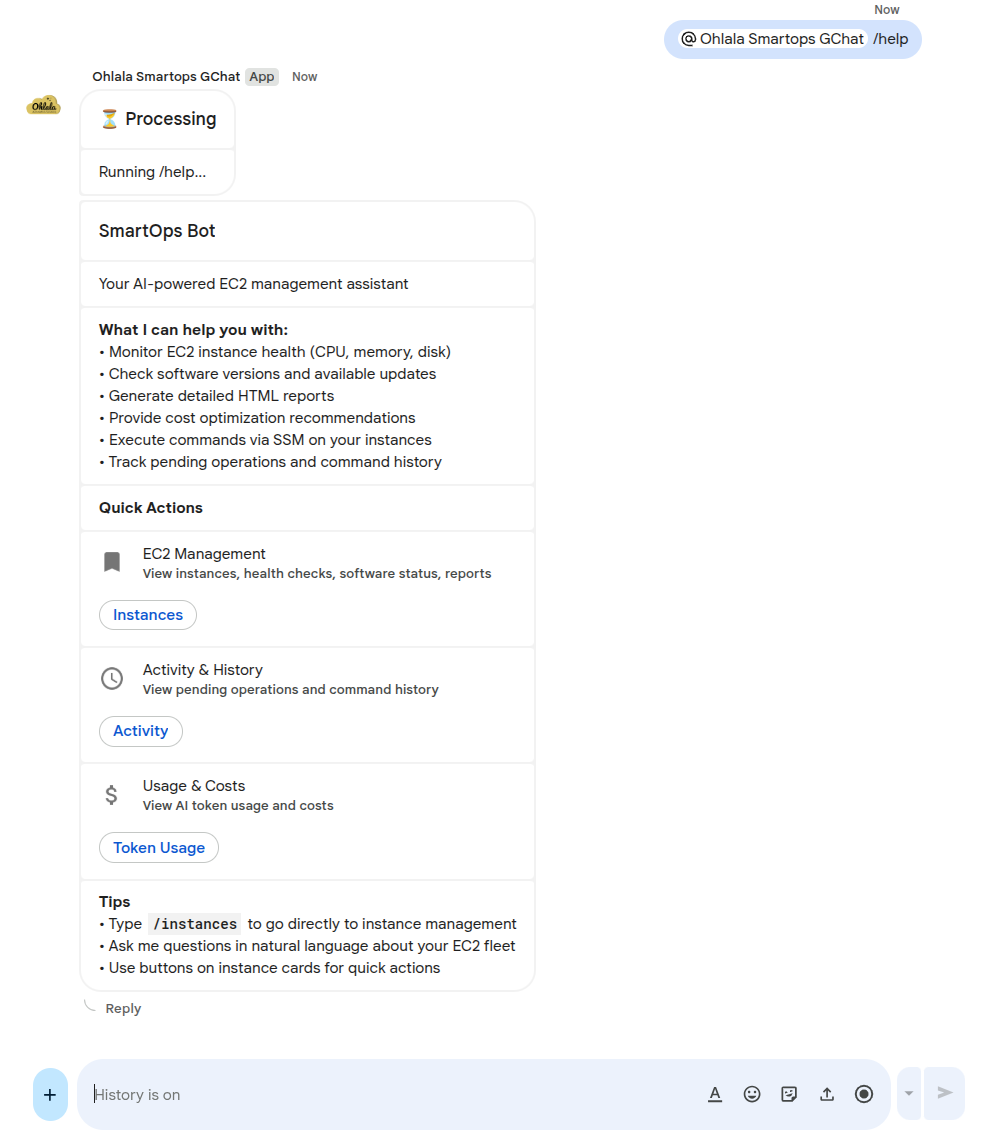
The bot should respond with a help card showing available commands.
Verify Integration
Check Google Chat API
- Go to Google Cloud Console
- Navigate to APIs & Services → Dashboard
- Find Google Chat API
- Click to see usage metrics
Check AWS CloudWatch Logs
- Go to CloudWatch → Log Groups
- Find
/aws/ecs/ohlala-smartops-...
- Look for logs containing
google-chat or incoming POST requests
- Verify requests are being received and processed
Monitor API Gateway
- Go to API Gateway Console
- Select your API
- Go to Dashboard
- You should see requests to
/api/google-chat endpoint
Troubleshooting
Bot Not Responding
Check Webhook URL
- Verify URL in Google Chat API Configuration matches CloudFormation output
- Ensure it includes the full path with
/api/google-chat
Check ECS Service
- Go to ECS Console
- Verify service has running tasks
- Check task logs for errors
Verify Google Chat is Enabled
- Check CloudFormation parameter
ChatPlatform is GoogleChat or Both
- Verify ECS task has the environment variable set
“App Not Found” in Search
Causes:
- App visibility not configured correctly
- You’re not in the allowed users/groups list
- App not yet published (may take a few minutes)
Solution:
- Go to Chat API Configuration
- Check Visibility settings
- Add your email to allowed users
- Wait a few minutes and try again
Authentication Errors
Symptoms: 401 or 403 errors in CloudWatch logs
Solution:
- Verify service account JSON was correct in CloudFormation
- Check the JSON was properly formatted (single line, no extra quotes)
- Verify Project ID matches the service account’s project
- Check Lambda authorizer logs for specific error messages
“Service Unavailable” Error
Causes:
- ECS task not running
- API Gateway misconfigured
- JWT validation failing
Solution:
- Check ECS service is running
- Verify API Gateway deployment
- Check CloudWatch logs for Lambda authorizer errors
- Verify the audience URL in Chat API Configuration matches your endpoint
Card Rendering Issues
Google Chat uses a different card format than Teams. If cards don’t render correctly:
- Check CloudWatch logs for card formatting errors
- Verify the QuickChart sidecar container is running in ECS
- Check S3 bucket for chart images (if using charts)
Google Chat vs Teams Differences
| Feature |
Google Chat |
Microsoft Teams |
| Card Format |
Google Card JSON |
Adaptive Cards |
| Authentication |
Service Account + JWT |
Azure AD + Bot Framework |
| Charts |
Uploaded to S3 as images |
Rendered inline |
| Message Updates |
Limited support |
Full support |
| @mentions |
Required in spaces |
Optional |
Success Checklist
Confirm everything is working:
Next Step
Your bot is connected to Google Chat! Now verify everything is working:
Continue to Verification & Testing →
1.9 - Verification & Testing
Confirm your deployment and run first commands
Deployment Checklist
Before testing commands, verify each component:
AWS Infrastructure
Microsoft Teams (if using Teams)
Google Chat (if using Google Chat)
Bedrock
Your First Commands
The commands below work in both Microsoft Teams and Google Chat. In Teams, use @Ohlala SmartOps to mention the bot. In Google Chat direct messages, you can type commands directly without mentioning.
1. Test Connection
Teams: @Ohlala SmartOps hello
Google Chat (direct message): hello
Expected Response: Friendly greeting confirming the bot is working
2. Get Help
Teams: @Ohlala SmartOps help
Google Chat: /help
Expected Response: Interactive card with available commands and examples
3. Check Instance Status
show me my EC2 instances
Expected Response: List of your EC2 instances with status information
4. Health Report
/health
Expected Response: Detailed health metrics for your instances
5. Natural Language Query
which instances are running in us-east-1?
Expected Response: Filtered list based on your query
Advanced Testing
Test SSM Integration
@Ohlala SmartOps check disk space on i-1234567890abcdef0
- Verifies SSM command execution
- Returns disk usage information
Test Cost Analysis
@Ohlala SmartOps analyze my EC2 costs
- Checks CloudWatch metrics access
- Provides cost optimization suggestions
Test Multi-Instance Commands
@Ohlala SmartOps show me all stopped instances
- Tests filtering and analysis capabilities
- Demonstrates natural language understanding
Monitoring Your Deployment
CloudWatch Metrics
Monitor key metrics in CloudWatch:
-
ECS Service
- CPU utilization (should be <50%)
- Memory utilization (should be <70%)
- Task count (should be 1)
-
API Gateway
- Request count
- 4XX/5XX errors (should be minimal)
- Latency (should be <3 seconds)
-
Bedrock Usage
- Token consumption
- API throttling events
- Model invocation errors
Common Issues & Solutions
Issue: Bot Not Responding
Quick Diagnosis:
# Check health endpoint
curl https://your-api.execute-api.region.amazonaws.com/prod-stackname/health
Solutions:
- Check ECS task is running
- For Teams: Verify webhook URL in Azure Bot configuration
- For Google Chat: Verify webhook URL in Chat API Configuration
- Ensure the app is installed correctly
- Review CloudWatch logs
Issue: “Model Access Required” Error
Symptom: Bot responds but shows Bedrock error
Solution:
- Go to Bedrock Console then Model access
- Enable Claude Sonnet 4.5
- Wait for “Access granted”
- Retry command (no restart needed)
Issue: No Instances Found
Symptom: Bot works but doesn’t see EC2 instances
Checks:
- Instances are in same region as deployment
- Instances have SSM agent installed
- IAM permissions are correct
- Try:
list all instances in all regions
Issue: Commands Timeout
Symptom: Bot shows “thinking” but never responds
Solutions:
- Check ECS task memory/CPU
- Look for Bedrock throttling
- Verify network connectivity
- Scale ECS service if needed
Issue: Teams Authentication Failures
Symptom: 401/403 errors in logs for Teams requests
Solutions:
- Regenerate Azure Bot credentials
- Update Secrets Manager
- Restart ECS service
- Check tenant ID is correct
Issue: Google Chat Authentication Failures
Symptom: 401/403 errors in logs for Google Chat requests
Solutions:
- Verify service account JSON is correctly formatted (single line)
- Check the service account has the correct permissions
- Verify the Project ID matches the service account
- Check the Authentication Audience setting in Chat API Configuration
Best Practices
- Start simple: Use basic commands first
- Be specific: Include instance IDs for targeted actions
- Use natural language: The bot understands context
- Review suggestions: Always verify before applying changes
Success Indicators
Your deployment is successful when:
- Bot responds within 2-3 seconds
- All test commands work
- No errors in CloudWatch logs
- Costs align with expectations
- Team members can use the bot
Next Steps
Now that your bot is working:
-
Explore Features
- Try advanced commands
- Experiment with natural language queries
- Review health and cost reports
-
Train Your Team
- Share the bot with team members
- Create usage guidelines
- Document common workflows
Getting Help
If you encounter issues:
-
Check Documentation
-
Contact Support
-
Community Resources
Congratulations
You’ve successfully deployed Ohlala SmartOps. Your AI-powered infrastructure assistant is ready to help manage your AWS environment through natural language conversations in Microsoft Teams, Google Chat, or both.
Happy automating!
2 - Architecture & Limitations
System architecture, design decisions, and current limitations of Ohlala SmartOps
Looking for deployment instructions? See the
Getting Started Guide for step-by-step deployment with screenshots.
System Architecture
High-Level Overview
Ohlala SmartOps follows a containerized, serverless architecture designed for high availability and cost efficiency:
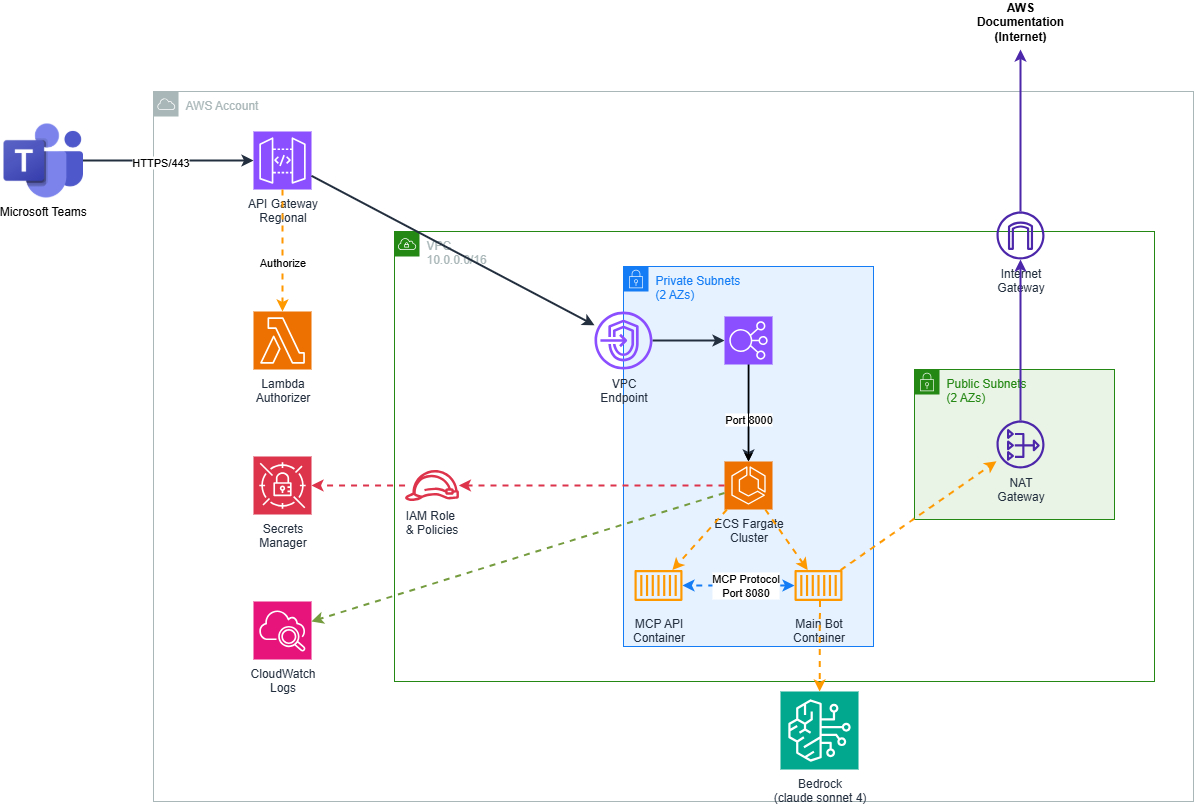
Container Architecture
Multi-Container Design with dedicated responsibilities:
Main Bot Container
- Purpose: Teams integration, conversation orchestration, Bedrock AI
- Port: 8000
- Resources: 768 CPU units, 1536MB memory
- Key Features:
- Microsoft Bot Framework integration
- Amazon Bedrock (Claude) orchestration
- Conversation state management
- Multi-language support
MCP AWS API Container
- Purpose: Secure AWS operations via Model Context Protocol
- Port: 8080
- Resources: 256 CPU units, 512MB memory
- Key Features:
- AWS service abstractions
- Permission-aware operations
- Rate limiting and retry logic
- Security-first design
Architecture Highlights
Fully Serverless
ECS Fargate + API Gateway eliminate infrastructure management overhead
- Zero server maintenance - AWS handles all patching and scaling
- Automatic scaling - Responds to demand without intervention
- Pay-per-use pricing - Only pay for actual compute time
- Note: ~30s cold start for new container instances
Security-First Design
Defense in depth with multiple security layers
- Private subnets - Containers have no direct internet exposure
- Isolated containers - Bot logic and AWS operations run separately
- JWT validation - Lambda authorizer validates all requests
- Secrets management - Credentials stored in AWS Secrets Manager
- Least privilege IAM - Each component has minimal required permissions
Microservices Architecture
Multi-container pattern for better maintainability
- Main bot container - Handles Teams interactions and AI orchestration
- MCP AWS container - Provides secure AWS API access
- Clear boundaries - Each container has a single responsibility
- Independent updates - Deploy changes without affecting other components
Stateless by Design
No persistent storage keeps architecture simple
- Reduced complexity - No database to manage or scale
- Lower costs - No database charges or backup requirements
- Horizontal scaling - Any container can handle any request
- Trade-off: Conversation context resets on container restart
Regional Flexibility
Deploy anywhere with single-region stacks
- Data sovereignty - Keep data in your required region
- Low latency - Deploy close to your EC2 instances
- Cost optimization - No cross-region data transfer fees
- Simple disaster recovery - Deploy multiple independent stacks
Optimized for Teams integration with enterprise-grade networking
- Network Load Balancer - Layer 4 load balancing for minimal latency
- VPC Link - Secure private connection from API Gateway
- Auto-scaling - Network automatically handles traffic spikes
- Health checks - Automatic failover for unhealthy containers
Response Times
- Health Check: < 1 second
- Simple Commands: 2-5 seconds
- AI Analysis: 5-15 seconds
- SSM Operations: 10-60 seconds (depending on command)
Throughput Limits
- Concurrent Users: 1-20 (single task)
- Commands/Day: 10,00+ (with proper scaling)
- API Gateway: 10,000 requests/second (AWS limit)
- Bedrock: 20 requests/minute per model (AWS limit)
Scaling Behavior
- Auto-scaling: ECS service set to auto-heal (1 task)
- Cold start: ~30 seconds for new tasks
Current Limitations
1. Session Management
- Issue: No persistent conversation history
- Impact: Context lost on container restart
- Workaround: Keep conversations short and focused
2. Multi-Region Support
- Issue: Single region deployment only
- Impact: No built-in disaster recovery
- Workaround: Deploy multiple stacks in different regions
5. Cold Start Latency
- Issue: 30+ second delay for new container starts
- Impact: First request after idle period is slow
- Workaround: Keep minimum 1 task running always
- Mitigation: ECS warmup targets available
Security Architecture
Network Security
- Private Subnets: Containers have no direct internet access
- Security Groups: Restrictive ingress/egress rules
- VPC Endpoints: Secure access to AWS services
Authentication & Authorization
- Teams Authentication: Microsoft Bot Framework JWT validation
- AWS Permissions: IAM roles with least-privilege access
- Inter-Container: Shared API key for MCP communication
- Secrets: AWS Secrets Manager for sensitive data
Data Protection
- Encryption in Transit: TLS 1.2+ for all communication
- Encryption at Rest: EBS volumes encrypted by default
- Logging: CloudWatch Logs with retention policies
- Audit Trail: All AWS API calls logged via CloudTrail
Technical References
Container Images
- Registry: Amazon ECR
- Repository:
709825985650.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/ohlala-automation-solutions/
- Tags: Version-based (v1.1.0 latest, earlier: v1.0.x)
Monitoring & Observability
- Metrics: CloudWatch Container Insights
- Logs: Structured JSON logging to CloudWatch
- Health Checks: HTTP endpoints on both containers
- Alarms: CPU, Memory, Error Rate monitoring
Backup & Recovery
- Container Images: Immutable, versioned in ECR
- Infrastructure: CloudFormation templates in version control
- Configuration: Environment variables and secrets
- No Persistent Data: Stateless design eliminates backup needs
Additional Resources
Need Help?
3 - SmartOps Features & Security
Comprehensive guide to Ohlala SmartOps features with emphasis on the approval system that ensures infrastructure safety
Safe and Simple
SmartOps is designed to be safe and easy to use. You can freely explore and ask questions - SmartOps will only execute commands when you explicitly approve them.
How Safety Works:
- Explore Freely: Ask any questions about your infrastructure
- Clear Explanations: SmartOps explains what actions will do before asking for approval
- Simple Approval: Just type ‘yes’ when you want to proceed with a command
- Complete Logging: All actions are logged for your records
Core Capabilities
Infrastructure Discovery
- Automatic EC2 Detection: Zero-configuration discovery of SSM-enabled instances
- Tag-Based Organization: Intelligent grouping by environment, application, and team
- Multi-Region Support: Manages instances across all supported AWS regions
Cost Intelligence
- Usage Analysis: Deep dive into actual vs. provisioned capacity
- AI-Powered Recommendations: ML-driven rightsizing suggestions
- Savings Calculations: Precise cost impact modeling with confidence intervals
Smart Troubleshooting
- AI-Guided Diagnostics: Step-by-step issue resolution assistance
- Remote Command Execution: Secure SSM-based command execution with approval
- Pattern Recognition: Intelligent problem identification and solution suggestions
On-Demand Analytics
- Health Assessments: Infrastructure status reports when requested
- Performance Insights: Capacity planning and optimization recommendations
- Custom Reports: Team-specific views and executive summaries
Detailed Feature Documentation
Comprehensive FinOps capabilities for EC2 cost management:
- Rightsizing recommendations with usage pattern analysis
- Reserved Instance planning and optimization
- Schedule-based scaling opportunities
- ROI calculations and savings tracking
On-demand monitoring and reporting features:
- Health reports and status dashboards
- Performance metrics and trend analysis
- Automated reporting and scheduled updates
- Custom analytics and team-specific views
Enterprise-grade security and audit capabilities:
- Approval system deep dive
- Complete audit trails and compliance reporting
- Identity and access management integration
- Security best practices and safeguards
AI & Safety Features
Intelligent Understanding
- Natural Language Processing: Understands context and intent
- Fuzzy Matching: Handles typos and variations in commands
- Context Awareness: Remembers conversation history for follow-ups
Safety by Design
- Read-First Policy: All operations require explicit confirmation
- Risk Assessment: AI evaluates potential impact before actions
- Audit Trail: Complete logging with user identity tracking
Quick Start
Try These Commands
@Ohlala SmartOps what instances do I have?
@Ohlala SmartOps show me a health report
@Ohlala SmartOps analyze my EC2 costs
@Ohlala SmartOps which instances need attention?
Best Practices
- Start with Read-Only: Explore monitoring features first
- Use Natural Language: Don’t worry about exact syntax
- Review Before Approving: Always check what commands will do
- Ask Follow-ups: Build on previous responses for context
Integration Capabilities
Native AWS Services
- EC2: Complete instance lifecycle management
- Systems Manager: Secure command execution
- CloudWatch: Metrics collection and analysis
- Cost Explorer: Detailed cost analysis
- Bedrock: AI-powered insights
- Microsoft Teams: Full-featured chat interface with Adaptive Cards
- Google Chat: Full-featured chat interface for Google Workspace users
- Azure AD / Google Workspace: Enterprise identity and access management
- Slack: Coming soon with comparable feature set
Key Benefits
Operational Efficiency
- Streamlined workflows with AI-powered assistance
- Faster incident response through automated discovery and analysis
- Reduced manual overhead for routine infrastructure tasks
Infrastructure Optimization
- Cost optimization recommendations based on actual usage patterns
- Right-sizing suggestions for underutilized resources
- Proactive monitoring to identify optimization opportunities
Next Steps
Explore Features in Detail
Get Started
Need Help?
4 - Bot Commands & Examples
Complete guide to Ohlala SmartOps chat commands and conversation examples for Microsoft Teams. Learn natural language patterns and see real responses.
Important: AI Response Variability
SmartOps uses AI to understand your requests, which means responses may vary slightly between similar questions. This natural variation makes conversations more intuitive, but our approval system ensures safety - any potentially dangerous operations require explicit confirmation before execution.
Command Overview
SmartOps understands both natural language and specific commands. You can interact in three ways:
- Natural Language: “Show me instances that are running high on CPU”
- Direct Commands: “list instances”, “health report”
- Contextual Queries: Follow-up questions based on previous responses
Safety Through Approval System
Security Spotlight: Approval Mechanism
SmartOps protects your infrastructure through a simple approval system:
- Safe Exploration: Ask any questions about your infrastructure
- Clear Explanations: The AI explains what each action will do before asking for approval
- Simple Confirmation: Just type ‘yes’ when you want to proceed with a command
- Complete Audit Trail: Every action is logged with user identity, timestamp, and results
This means you can safely explore and ask questions - the AI will only execute commands when you explicitly approve them.
Documentation Sections
Built-in commands for quick access to common operations:
- Essential commands (
/help, /status, /instances)
- Information commands (
/version, /regions, /limits)
- Utility commands (
/clear, /settings, /feedback)
- Support commands (
/debug, /contact)
Detailed examples of all available commands with natural language variations and expected responses:
- Instance management (list, describe, control)
- Health monitoring and troubleshooting
- Cost optimization and rightsizing
- Remote command execution
Learn how SmartOps understands context and intent:
- Context awareness and fuzzy matching
- Intent recognition patterns
- Follow-up conversations
- Handling typos and variations
Quick Start Commands
Try these commands to get started:
@Ohlala SmartOps help
@Ohlala SmartOps what instances do I have?
@Ohlala SmartOps show me a health report
Natural Language
@Ohlala SmartOps which instances need attention?
@Ohlala SmartOps how much am I spending on EC2?
@Ohlala SmartOps help me troubleshoot my web server
Follow-up Questions
After any response, you can ask follow-up questions like:
- “Show me more details about that”
- “What would you recommend?”
- “Can you help me fix this?”
Best Practices
- Start Simple: Begin with read-only commands to get familiar
- Use Natural Language: Don’t worry about exact syntax
- Ask Follow-ups: Build on previous responses for context
- Review Before Approving: Always check what commands will do
Next Steps
Need Help?
4.1 - Slash Commands Reference
Complete reference for built-in slash commands and their usage
Quick Tip: Slash commands start with / and provide instant responses. Use them for quick tasks and information lookup.
Essential Commands
/help
Purpose: Display all available commands and features
Usage: /help or /help [command] for detailed help on a specific command
Response: Interactive adaptive card showing:
- All available slash commands
- Natural language command examples
- Quick action buttons for common operations
- Localized content based on user’s Teams language

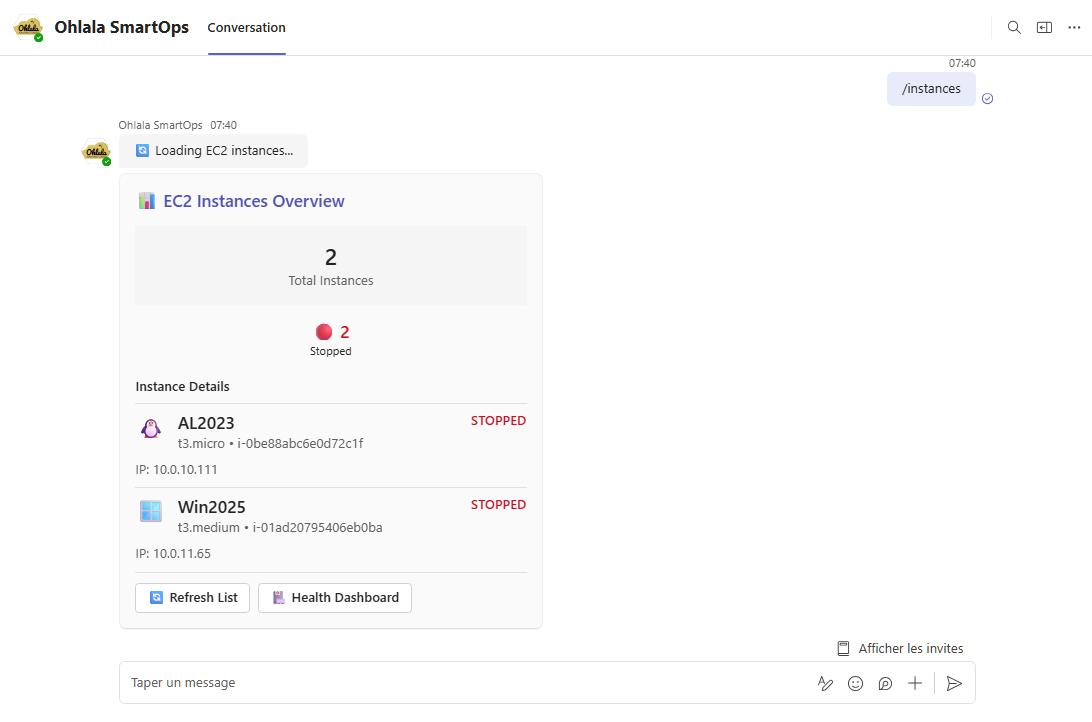
/instances
Purpose: List all EC2 instances with interactive management options
Usage: /instances
Response: Interactive card displaying:
- Instance IDs, names, and tags
- Current state (running, stopped, etc.)
- Instance type and platform
- SSM connectivity status
- Quick action buttons for each instance
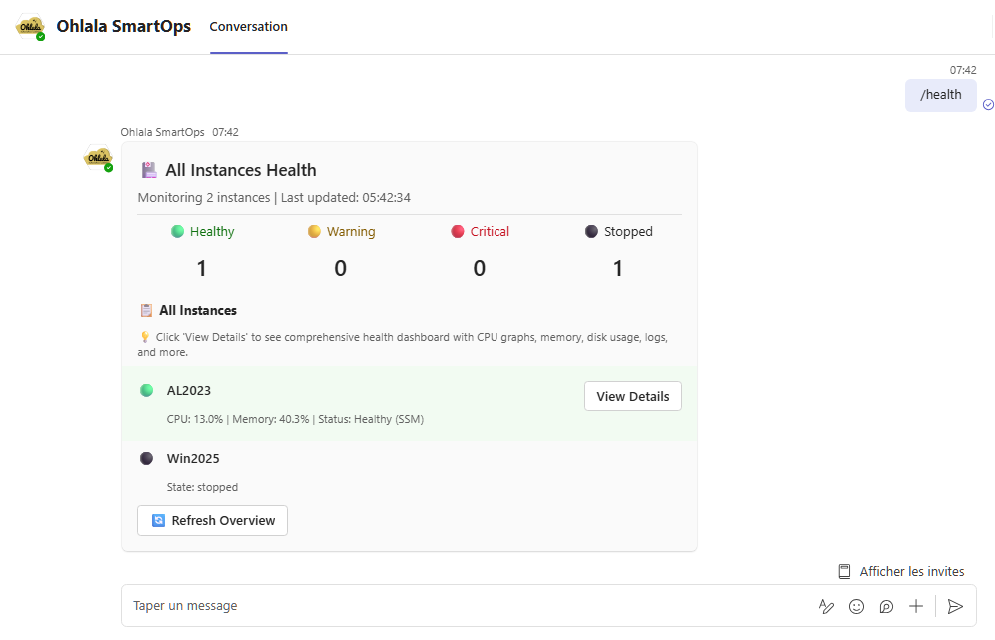
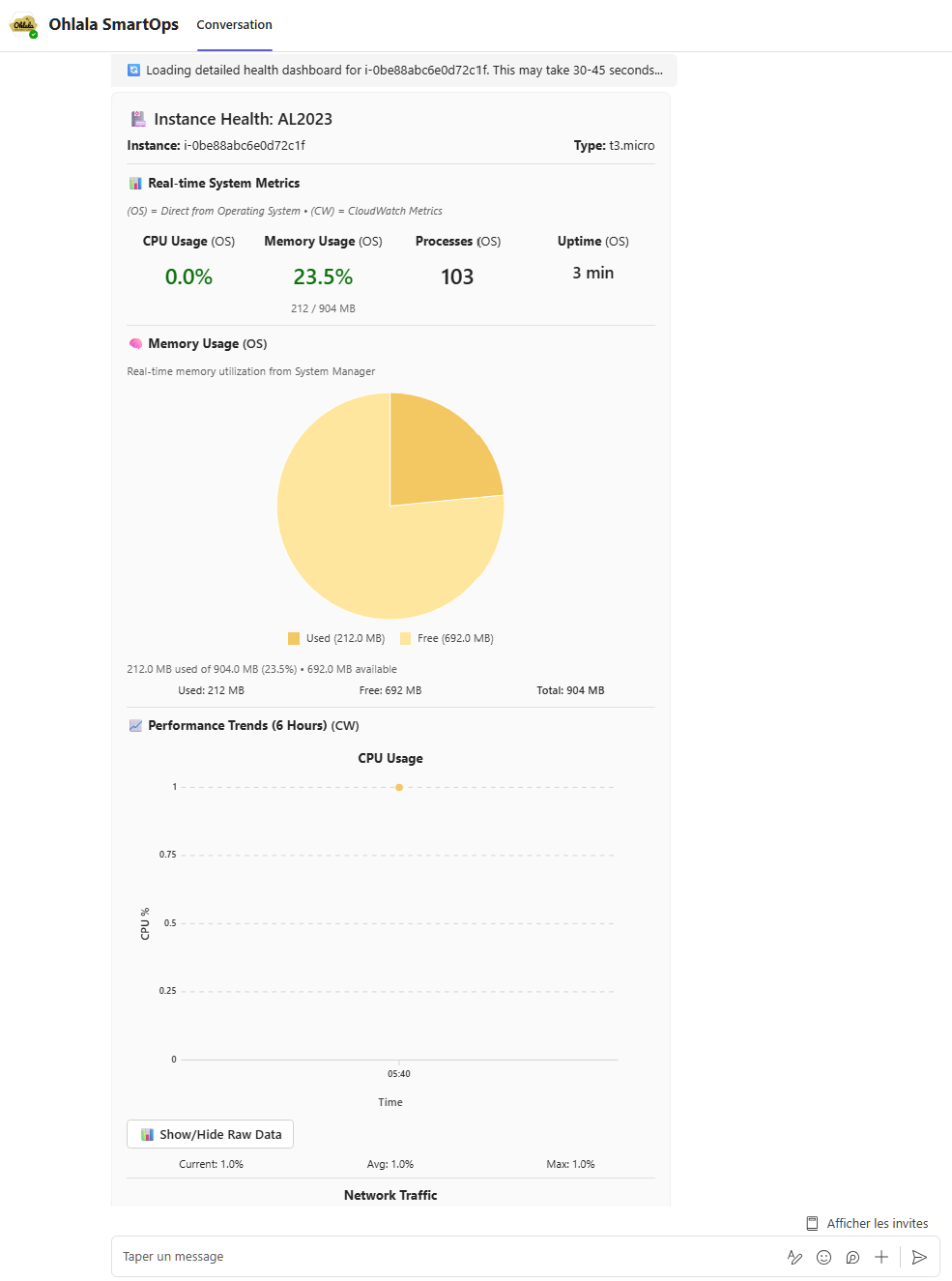
/health
Purpose: Comprehensive health dashboard for instances
Usage: /health for all instances, or /health [instance-id] for a specific instance
Response: Rich dashboard featuring:
- CPU, memory, and disk usage metrics
- SSM agent connectivity status
- Visual health indicators and charts
- System performance trends
- CloudWatch metrics integration
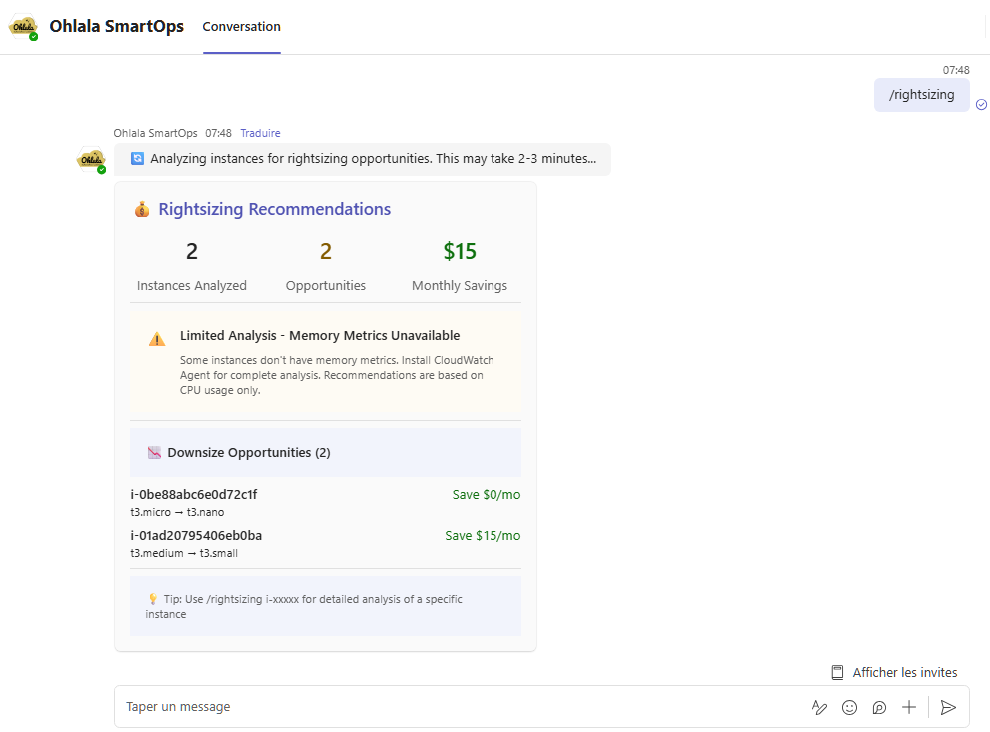
/rightsizing
Purpose: Cost optimization and rightsizing recommendations
Usage: /rightsizing
Response: Cost optimization dashboard with:
- Current instance utilization analysis
- Rightsizing recommendations
- Potential cost savings calculations
- Instance type upgrade/downgrade suggestions
- CloudWatch metrics-based insights
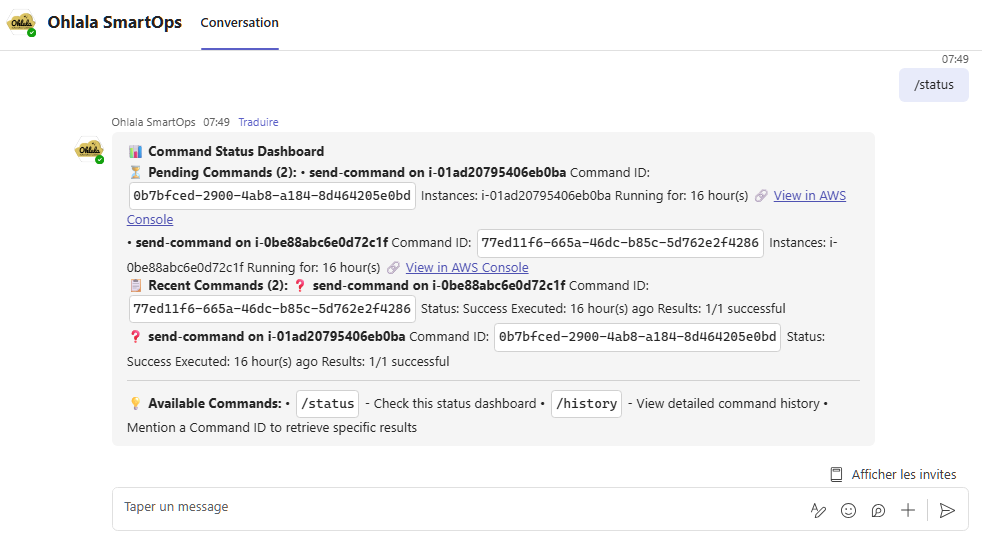
Monitoring & Management Commands
/status
Purpose: Show pending commands and recent activity
Usage: /status
Response: Command status dashboard showing:
- Currently pending SSM commands
- Recent command execution history
- Command success/failure rates
- AWS Console links for detailed monitoring
- Elapsed time for running operations
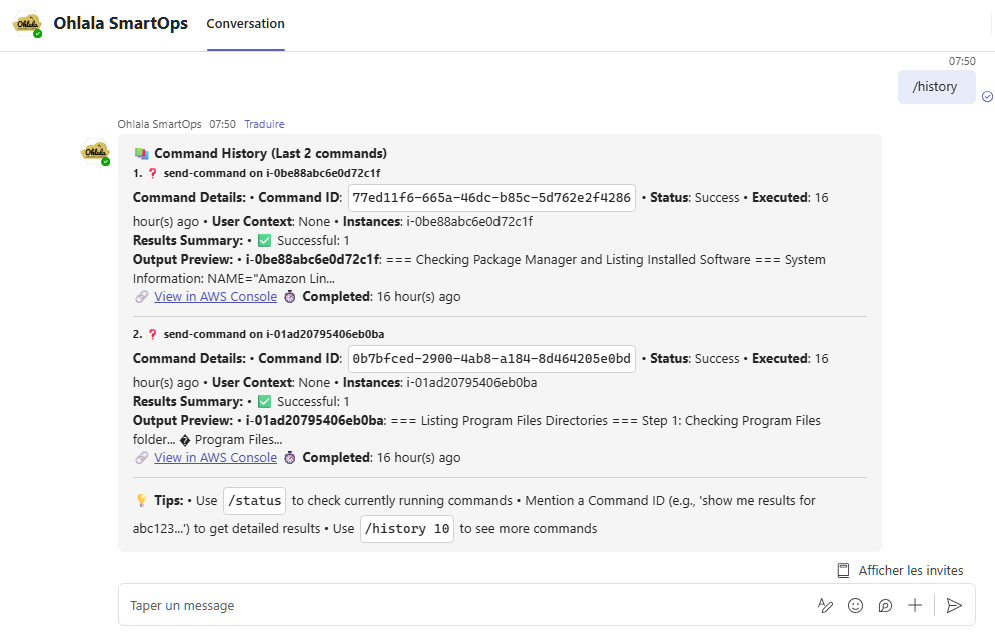
/history
Purpose: View detailed command execution history
Usage: /history
Response: Comprehensive command history with:
- Past command executions
- Success/failure status
- Detailed results and outputs
- Timestamp and user information
- Filtering and search capabilities
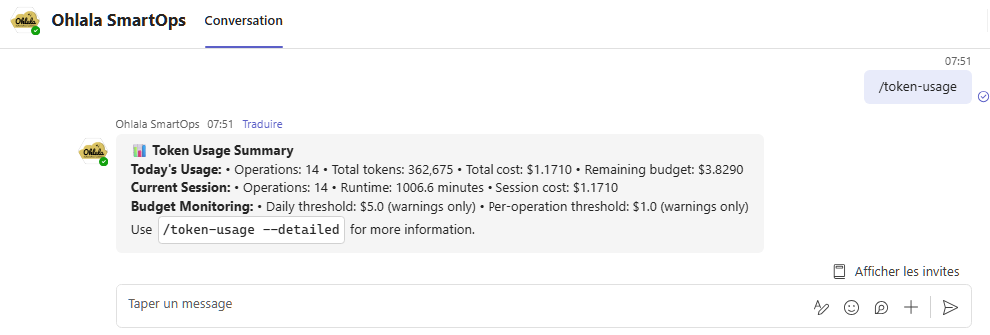
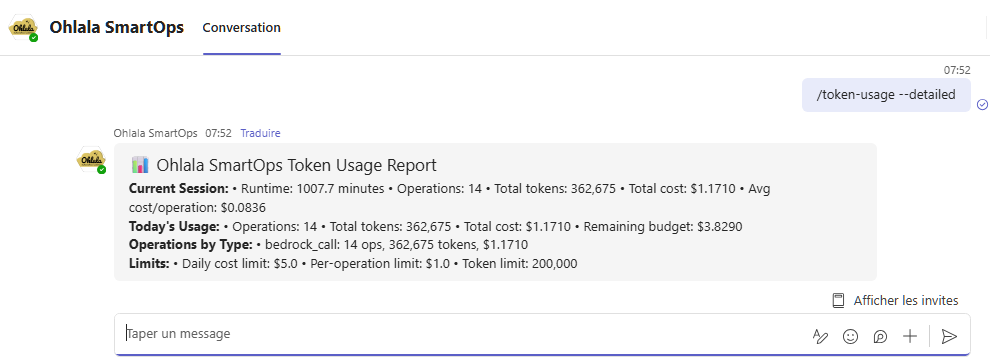
/token-usage
Purpose: Monitor Bedrock AI token usage and costs
Usage: /token-usage
Response: Token usage analytics including:
- Current billing period usage
- Token consumption trends
- Cost breakdown by operation type
- Usage limits and quotas
- Optimization recommendations
Command Tips
Quick Access
- Type
/ in Teams to see all available slash commands
- Commands are case-insensitive:
/help = /HELP = /Help
- Use Tab completion in Teams for faster command entry
Combining with Natural Language
You can follow slash commands with natural language for more specific requests:
/health show me only instances with high CPU usage
/instances filter by production environment
/help with cost optimization
Command Parameters
- Most commands work without parameters for overview information
- Add instance IDs for specific instance details:
/health i-1234567890abcdef0
- Use
/help [command] for detailed usage instructions
Command History
- Use ↑ (up arrow) in Teams to repeat recent commands
- All commands are logged for audit purposes
- Interactive cards maintain state for better user experience
Command Comparison
| Command |
Speed |
Detail Level |
Best For |
/instances |
Fast |
Interactive |
Instance management |
"show me my instances" |
Slower |
Conversational |
Analysis & insights |
/health |
Fast |
Dashboard |
Health monitoring |
"which instances need attention?" |
Slower |
AI Analysis |
Troubleshooting |
/status |
Fast |
Current |
Operation tracking |
Error Handling
Common Issues
Command not recognized:
Unknown command: /instaces
Did you mean: /instances?
Missing permissions:
❌ Insufficient AWS permissions for this operation
Contact your administrator to review IAM policies
Service unavailable:
⚠️ AWS services temporarily unavailable
Try again in a few moments or use /status for details
Recovery Steps
- Check spelling - Commands must be exact
- Verify AWS permissions - Commands require proper IAM roles
- Try
/status - Check if services are operational
- Use
/help - See all available commands
Next Steps
Learn More
Quick Start
Try these commands right now in Teams:
/help - See what’s available/instances - View your EC2 instances with interactive controls/health - Check instance health dashboard/rightsizing - Discover cost optimization opportunities"show me instances that need attention" - Try natural language
Advanced Usage
Command Workflows
Combine slash commands for powerful workflows:
/instances → Click instance → View health details/health → Identify issues → Use natural language for troubleshooting/rightsizing → Review recommendations → Ask for implementation help/status → Monitor ongoing operations → /history for detailed results
Interactive Features
- Action Buttons: Most commands include interactive buttons for common actions
- Context Preservation: Commands remember your selections for follow-up questions
- Real-time Updates: Health and status information refreshes automatically
- Multi-language Support: Commands adapt to your Teams language preference
Need Help?
4.2 - Command Examples & Usage
Detailed examples of all SmartOps commands with natural language variations and expected responses for EC2 management in Teams.
Command Categories
Instance Management
List Instances
Shows all EC2 instances with current status and basic metrics.
Natural Language Examples:
- “What instances do I have?”
- “Show me all EC2 instances”
- “List my servers”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps list instances
Response Format:
📊 EC2 Instance Summary
Found 5 instances in us-east-1
✅ web-server-01 (i-0abc123def)
Type: t3.medium | State: running
CPU: 45% | Memory: 62% | Disk: 38%
⚠️ database-01 (i-0def456ghi)
Type: m5.large | State: running
CPU: 78% | Memory: 85% | Disk: 72%
[... more instances ...]
Get Instance Details
Detailed information about a specific instance.
Natural Language Examples:
- “Tell me about instance i-0abc123def”
- “Show details for web-server-01”
- “What’s the configuration of my database server?”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps describe instance <instance-id>
Response Format:
📋 Instance Details: web-server-01
Instance ID: i-0abc123def
Type: t3.medium (2 vCPU, 4 GB RAM)
State: running (since 2024-03-15 10:30 UTC)
Platform: Amazon Linux+
AZ: us-east-1a
Private IP: 10.0.1.45
Public IP: 54.123.45.67
Tags:
- Name: web-server-01
- Environment: production
- Team: platform
Monitoring:
- CPU: 45% (avg last hour)
- Memory: 62% (current)
- Network In: 125 MB/hour
- Network Out: 450 MB/hour
Health Monitoring
Health Report
Comprehensive health status of all instances.
Natural Language Examples:
- “Show me the health report”
- “How healthy are my instances?”
- “Give me a status update”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps health report
Response Format:
🏥 Infrastructure Health Report
Generated: 2024-03-20 14:30 UTC
Overall Health: ⚠️ ATTENTION NEEDED
Summary:
✅ Healthy: 12 instances
⚠️ Warning: 3 instances
❌ Critical: 1 instance
Issues Requiring Attention:
❌ CRITICAL: app-server-03
- CPU: 95% (sustained for 30 min)
- Action: Consider scaling or investigating process
⚠️ WARNING: database-01
- Disk: 85% full
- Action: Clean up logs or expand storage
⚠️ WARNING: web-cache-02
- Memory: 88% utilized
- Action: Monitor for OOM issues
📈 Trends:
- CPU usage up 15% from yesterday
- 2 new instances added this week
- Cost trending 8% over budget
Instance Health Check
Check health of specific instance.
Natural Language Examples:
- “Is web-server-01 healthy?”
- “Check the health of i-0abc123def”
- “How is my database server doing?”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps check health <instance-id>
Cost Optimization
Cost Analysis
Analyze EC2 costs and identify savings opportunities.
Natural Language Examples:
- “Analyze my EC2 costs”
- “Where can I save money?”
- “Show me cost optimization opportunities”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps cost analysis
Response Format:
💰 EC2 Cost Analysis Report
Period: Last 30 days
Current Spending:
- Total: $3,456.78
- On-Demand: $2,890.45 (84%)
- Reserved: $566.33 (16%)
- Spot: $0.00 (0%)
Top Recommendations:
1. 🎯 Right-size Overprovisioned Instances
Potential Savings: $456/month (13%)
- web-server-01: t3.medium → t3.small
Current: 15% CPU avg → Save $28/month
- test-server-02: m5.xlarge → m5.large
Current: 8% CPU avg → Save $95/month
2. 💼 Purchase Reserved Instances
Potential Savings: $890/month (26%)
- 5 instances running 24/7
- Recommend 1-year no upfront RIs
3. 🌙 Implement Schedule-Based Scaling
Potential Savings: $234/month (7%)
- Dev/test instances can be stopped nights/weekends
- 10 instances identified
Total Potential Savings: $1,580/month (46%)
Rightsizing Recommendations
Get specific rightsizing suggestions.
Natural Language Examples:
- “Which instances should I rightsize?”
- “Show me oversized instances”
- “Find underutilized servers”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps rightsizing recommendations
Troubleshooting
Troubleshoot Instance
AI-guided troubleshooting for instance issues.
Natural Language Examples:
- “My web server is slow”
- “Help me troubleshoot i-0abc123def”
- “Database connections are timing out”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps troubleshoot <instance-id>
Interactive Response:
🔧 Troubleshooting Assistant
I'll help you troubleshoot web-server-01. Let me gather some information...
Current Status:
- Instance is running
- CPU: 45% (normal)
- Memory: 92% (HIGH)
- Disk I/O: Normal
- Network: Normal
⚠️ High memory usage detected!
Let me check what's consuming memory...
[Running diagnostic commands via SSM]
Top Memory Consumers:
1. java process: 2.8 GB (70%)
2. mysql: 650 MB (16%)
3. nginx: 120 MB (3%)
Recommendations:
1. Immediate: Restart the Java application
2. Short-term: Increase instance type to t3.large
3. Long-term: Investigate memory leak in application
Would you like me to:
A) Restart the Java application now
B) Show application logs
C) Create a snapshot before changes
Find Issues
Identify instances with problems.
Natural Language Examples:
- “Which instances need attention?”
- “Show me problematic servers”
- “Find unhealthy instances”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps find issues
Remote Execution
Execute Command
Run commands on instances via SSM.
Natural Language Examples:
- “Run ‘df -h’ on web-server-01”
- “Check disk space on all instances”
- “Restart nginx on the web servers”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps execute "<command>" on <instance-id>
Safety Features:
- Confirmation required for all SSM commands
- Commands run with limited privileges
- Audit trail maintained
- Output limited to 24,000 characters
Response Format:
🔨 Command Execution Request
Target: web-server-01 (i-0abc123def)
Command: systemctl restart nginx
⚠️ This command will restart the nginx service.
This may cause brief downtime.
Type 'yes' to confirm execution
[After confirmation]
✅ Command Executed Successfully
Output:
nginx.service - The nginx HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2024-03-20 15:45:32 UTC
Execution Time: 1.2 seconds
Command ID: abc-def-ghi-123
Instance Control
Start Instance
Start stopped instances.
Natural Language Examples:
- “Start web-server-01”
- “Boot up the test environment”
- “Turn on i-0abc123def”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps start instance <instance-id>
Stop Instance
Stop running instances.
Natural Language Examples:
- “Stop the dev server”
- “Shut down test-instance-02”
- “Turn off i-0abc123def”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps stop instance <instance-id>
Safety Confirmation:
⚠️ Stop Instance Confirmation
You're about to stop: prod-database-01
Environment: production
Current connections: 45
This action will:
- Terminate all active connections
- Stop the instance (data on instance store volumes will be lost)
- Incur no further hourly charges
Type 'yes' to confirm stopping this instance
Reboot Instance
Restart instances gracefully.
Natural Language Examples:
- “Reboot web-server-01”
- “Restart my application server”
- “Perform a soft reset on i-0abc123def”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps reboot instance <instance-id>
Scheduling
Schedule Report
Set up automated daily reports.
Natural Language Examples:
- “Send me a daily health report at 9 AM”
- “Schedule cost reports every Monday”
- “Set up morning status updates”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps schedule daily report at <time>
Get Help
Show available commands and usage.
Natural Language Examples:
- “Help”
- “What can you do?”
- “Show me available commands”
Direct Command: @Ohlala SmartOps help
Response Format:
🤖 Ohlala SmartOps - Command Reference
I understand natural language! Just describe what you need.
You can also use these commands:
📊 Monitoring
• list instances - Show all EC2 instances
• health report - Comprehensive health status
• check health <id> - Check specific instance
💰 Cost Optimization
• cost analysis - Analyze spending
• rightsizing recommendations - Find savings
🔧 Troubleshooting
• troubleshoot <id> - AI-guided diagnostics
• find issues - Identify problems
🔨 Remote Execution
• execute "<command>" on <id> - Run via SSM
⚙️ Instance Control
• start/stop/reboot instance <id>
📅 Scheduling
• schedule daily report at <time>
💡 Tips:
- Use instance names or IDs
- Ask follow-up questions
- Natural language works best!
Need more help? Visit docs.ohlala.cloud
Advanced Features
Bulk Operations
Execute commands across multiple instances:
@Ohlala SmartOps execute “sudo yum update -y” on tag:Environment=dev
Filtering
Filter instances by various criteria:
@Ohlala SmartOps list instances where cpu > 80%
@Ohlala SmartOps find instances tagged Environment=production
Chaining Commands
Combine multiple operations:
@Ohlala SmartOps stop all dev instances then create ami backups
Next Steps
Need Help?
4.3 - Natural Language Processing
Learn how SmartOps understands context and intent through natural language processing, fuzzy matching, and conversational AI.
AI Response Variability
SmartOps uses AI to understand your requests, which means responses may vary slightly between similar questions. This natural variation makes conversations more intuitive, but our approval system ensures safety - any potentially dangerous operations require explicit confirmation before execution.
Natural Language Processing Features
SmartOps uses Amazon Bedrock’s Claude AI to understand context and intent. Examples:
Context Awareness
User: "Show me expensive instances"
Bot: [Lists instances sorted by cost]
User: "Which of those can be rightsized?"
Bot: [Understands "those" refers to expensive instances]
Intent Recognition
User: "My website is down"
Bot: "I'll help troubleshoot. Let me check your web servers..."
[Automatically identifies web-tagged instances and checks health]
Fuzzy Matching
User: "Check the databse server"
Bot: "Checking database-server-01..."
[Handles typos and variations]
How SmartOps Understands You
1. Intent Classification
SmartOps recognizes different types of requests:
Information Requests:
- “What instances do I have?”
- “Show me the current status”
- “How much am I spending?”
Action Requests:
- “Restart the web server”
- “Stop the test instances”
- “Update all development servers”
Troubleshooting Requests:
- “My application is slow”
- “Why is the database not responding?”
- “Help me fix this error”
2. Context Tracking
SmartOps remembers conversation context:
Example Conversation:
User: "List my production instances"
Bot: [Shows 5 production instances]
User: "Which one has the highest CPU?"
Bot: "Among your production instances, web-prod-02 has the highest CPU at 78%"
User: "Show me more details about that one"
Bot: [Shows detailed info for web-prod-02]
User: "Can you help me optimize it?"
Bot: "I can help optimize web-prod-02. Let me analyze its usage patterns..."
3. Entity Recognition
SmartOps identifies specific entities in your requests:
Instance References:
- Instance IDs: “i-0abc123def”
- Instance names: “web-server-01”
- Tags: “all production instances”
- Roles: “database servers”, “web servers”
Time References:
- “last week”, “yesterday”, “this month”
- “since 9 AM”, “in the past hour”
Metric References:
- “high CPU”, “low memory”, “disk space”
- “expensive instances”, “underutilized servers”
Conversation Patterns
Follow-up Questions
After any response, you can ask natural follow-ups:
After Health Report:
- “What’s causing the high CPU on server-01?”
- “How can I fix the memory issue?”
- “Should I be worried about that warning?”
After Cost Analysis:
- “How much would rightsizing save me?”
- “Which instances should I prioritize?”
- “Can you help me implement those recommendations?”
After Instance List:
- “Which ones need updates?”
- “Show me only the problematic ones”
- “What would you recommend for optimization?”
Conversational Shortcuts
SmartOps understands casual language:
Informal Requests:
- “What’s up with my servers?” → Health status check
- “How are things looking?” → Overall status report
- “Any issues I should know about?” → Problem identification
- “Can you help me save money?” → Cost optimization analysis
Implicit Context:
- “Restart it” (after discussing a specific instance)
- “Show me more” (after any report or list)
- “What do you think?” (asking for AI recommendations)
Advanced Language Features
Comparative Queries
User: "Which instances use more CPU than database-01?"
User: "Show me servers that cost more than $100/month"
User: "Find instances smaller than t3.medium"
Temporal Queries
User: "What happened to web-server-01 yesterday?"
User: "Show me cost trends over the last 3 months"
User: "Which instances were restarted this week?"
Conditional Logic
User: "If the CPU is over 80%, show me the top processes"
User: "When database connections exceed 50, check memory usage"
User: "Alert me if any production instance goes down"
Aggregation Requests
User: "Total cost of all development instances"
User: "Average CPU across web servers"
User: "Count of instances by environment"
Handling Ambiguity
When your request is unclear, SmartOps will ask for clarification:
Example Ambiguous Requests:
User: "Restart the server"
Bot: "I found 5 servers. Which one would you like me to restart?
- web-server-01 (production)
- web-server-02 (production)
- app-server-01 (staging)
- db-server-01 (production)
- test-server-01 (development)"
User: "Stop the expensive instances"
Bot: "I found 3 instances with costs over $200/month. Would you like to:
A) See details about these instances first
B) Stop all 3 instances
C) Stop only non-production instances"
Error Recovery
SmartOps handles common communication issues:
Typos and Misspellings
User: "chck the helth of web-srvr-01"
Bot: "Checking the health of web-server-01..."
[Automatically corrects and understands intent]
Incomplete Requests
User: "show instances"
Bot: "Here are your EC2 instances. Would you like me to:
- Show more details about any specific instance
- Filter by environment or status
- Include cost or performance information"
Mixed Languages (Limited)
User: "montrer les instances"
Bot: "I understand you want to see instances. Here are your EC2 instances..."
[Basic French recognition, responds in English]
Learning from Context
SmartOps learns patterns within a conversation:
Preference Learning
User: "Show instances without IDs"
Bot: [Remembers preference for this conversation]
User: "Now show the database servers"
Bot: [Lists database servers without IDs, as previously requested]
Domain Knowledge
SmartOps understands infrastructure terminology:
Technical Terms:
- “Load balancer”, “auto-scaling group”, “availability zone”
- “RDS”, “EBS”, “VPC”, “security group”
- “Production”, “staging”, “development” environments
Common Patterns:
- “Scale up/down”, “failover”, “backup”
- “Peak hours”, “maintenance window”, “scheduled downtime”
- “Performance bottleneck”, “capacity planning”
Best Practices for Natural Communication
1. Be Conversational
- Use natural language like you’re talking to a colleague
- Don’t worry about exact command syntax
- Feel free to ask follow-up questions
2. Provide Context
- Mention environment: “production servers”, “dev instances”
- Include timeframes: “since yesterday”, “this week”
- Specify scope: “all web servers”, “just the database”
3. Ask for Clarification
- If responses aren’t what you expected, ask for clarification
- Request more details: “Can you explain that further?”
- Ask for alternatives: “What other options do I have?”
4. Build on Previous Responses
- Use “that instance”, “those servers”, “the expensive ones”
- Ask follow-ups: “What would you recommend?”, “Should I be concerned?”
Integration with Commands
Natural language seamlessly integrates with command execution:
User: "The production web servers seem slow, can you help?"
Bot: "I'll investigate your production web servers. Let me check their current status...
Found 3 production web servers:
- web-prod-01: CPU 45%, Memory 78%
- web-prod-02: CPU 89%, Memory 92% ⚠️
- web-prod-03: CPU 52%, Memory 65%
web-prod-02 appears to have high resource usage. Would you like me to:
A) Show detailed process information
B) Restart the web services
C) Investigate recent logs
D) Recommend instance scaling"
Next Steps
Need Help?
5 - Troubleshooting Guide
Solutions for common issues with Ohlala SmartOps deployment, Teams integration, and daily operations. Find quick fixes and detailed debugging steps.
Quick Diagnostics
Run this checklist to identify common issues:
-
Check Service Health
curl https://your-api-gateway-url/prod-{StackName}/health
Expected: {"status": "healthy"}
-
Verify CloudFormation Stack
- AWS Console → CloudFormation
- Stack status:
CREATE_COMPLETE or UPDATE_COMPLETE
-
Check ECS Service
- AWS Console → ECS → Clusters
- Service should have 1 running task
-
Review Recent Logs
- AWS Console → CloudWatch → Log Groups
- Check
/aws/ecs/ohlala-smartops-{StackName}
CloudWatch Logs Troubleshooting
Quick Log Analysis
Most issues can be diagnosed by checking CloudWatch logs for ERROR messages in the ECS task logs.
1. Access ECS Task Logs
Via AWS Console:
- Go to CloudWatch → Log Groups
- Find
/aws/ecs/ohlala-smartops-{your-stack-name}
- Click on the most recent log stream
- Search for “ERROR” using Ctrl+F
Bot Not Responding
Symptoms
- No response when messaging the bot in Teams
- Bot appears offline
- Commands timeout without response
Solution 1: Verify Webhook Configuration
-
Check Webhook URL
# Get from CloudFormation outputs
aws cloudformation describe-stacks \
--stack-name your-stack-name \
--query "Stacks[0].Outputs[?OutputKey=='TeamsWebhookURL'].OutputValue" \
--output text
-
Update in Azure Bot
- Azure Portal → Your Bot → Configuration
- Messaging endpoint must match CloudFormation output
- Must end with
/api/messages
Solution 2: Check Authentication
-
Verify Secrets in AWS
aws secretsmanager get-secret-value \
--secret-id ohlala-smartops-teams-{StackName} \
--query SecretString \
--output json
-
Validate Credentials Match Azure
- App ID must match Azure Bot’s App ID
- Password must be valid and not expired
- Tenant ID must match your Azure AD
-
Check Lambda Authorizer Logs
- CloudWatch → Log Groups →
/aws/lambda/ohlala-authorizer-{StackName}
- Look for “Authorization failed” messages
Solution 3: Teams App Issues
-
Re-upload Teams Package
- Remove existing app from Teams
- Download fresh package
- Update manifest.json with correct bot ID
- Re-upload to Teams
- You may need to manually bump the version in manifest.json to force Teams to accept the update
-
Check Teams Policies
- Teams Admin Center → Teams apps → Permission policies
- Ensure custom apps are allowed
- Check user has permission to use bots
Deployment Failures
Error: “CREATE_FAILED - Resource handler returned message: ‘The specified subnet does not exist’”
Solution:
# For Existing VPC mode, verify subnet IDs
aws ec2 describe-subnets \
--subnet-ids subnet-xxxxx \
--region your-region
Error: “CREATE_FAILED - IAM role already exists”
Solution:
# Delete existing role or use different stack name
aws iam delete-role --role-name ec2-management-bot-execution-role
aws iam delete-role --role-name ec2-management-bot-task-role
ECS Task Won’t Start
Error: “ResourceInitializationError: unable to pull secrets or registry auth”
Solution:
- Check ECR permissions
- Verify marketplace subscription is active
- Check execution role has secret access:
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name ec2-management-bot-execution-role \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonECSTaskExecutionRolePolicy
Bedrock Model Issues
Error: “ValidationException: The provided model identifier is invalid”
This is the #1 most common deployment issue!
Cause: Amazon Bedrock Claude Sonnet 4.5 model access is not enabled or not available in your deployment region.
Solution:
-
Navigate to Amazon Bedrock Console
- Go to AWS Console → Amazon Bedrock
- Ensure you’re in the correct region (same as deployment)
-
Enable Claude Sonnet 4.5 Model Access
- Left sidebar → “Model access”
- Click “Edit” or “Manage model access”
- Find Anthropic section
- Enable Claude Sonnet 4.5:
- Claude Sonnet 4.5 (anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-*)
-
Submit Request
- Click “Next” → “Submit”
- Most requests are approved immediately
- Wait for status to show “Available”
-
Verify Access
# Test via AWS CLI
aws bedrock list-foundation-models \
--region us-east-1 \
--query 'modelSummaries[?contains(modelId, `claude-sonnet`)]'
-
Test in Bedrock Playground
- Bedrock Console → Playgrounds → Chat
- Select Claude Sonnet 4.5
- Send test message: “Hello”
- Should receive response
-
Restart Application (if already deployed)
# Force ECS service restart
aws ecs update-service \
--cluster your-cluster \
--service your-service \
--force-new-deployment
Regional Support with Cross-Region Inference Profiles:
Cross-Region Support
Ohlala SmartOps now supports ALL AWS regions through intelligent inference profile selection, including regions without native Claude Sonnet 4.5 support like eu-west-3.
Primary Regions (Native Claude Sonnet 4.5 Support):
- us-east-1 (Recommended)
- us-west-2
- eu-west-1
- eu-central-1
- ap-northeast-1
- ap-southeast-2
Supported via Inference Profiles:
- eu-west-3 (via global/EU inference profiles)
- eu-west-2 (via global/EU inference profiles)
- eu-north-1 (via global/EU inference profiles)
- ap-southeast-1 (via global/APAC inference profiles)
- ap-northeast-2 (via global/APAC inference profiles)
- ap-south-1 (via global/APAC inference profiles)
- ca-central-1 (via global inference profiles)
- sa-east-1 (via global inference profiles)
How Inference Profiles Work:
- Global Profile:
global.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-* - Works from any region
- Regional Profiles:
eu.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-* - Optimized for EU regions
- Automatic Fallback: Application automatically tries the best profile for your region
For eu-west-3 Specifically:
- The application will automatically use global or EU inference profiles
- No additional configuration required
- Same Claude Sonnet 4.5 quality and performance
Error: “AccessDeniedException: You do not have access to the requested model”
Cause: Model access requested but not yet approved, or using wrong model ID.
Solution:
-
Check approval status:
- Bedrock Console → Model access
- Status should be “Available”, not “Pending”
-
Wait for approval:
- Standard models: Usually immediate
- Advanced models: Up to 24-48 hours
- Check email for approval notification
Permission Issues
Solution:
- Add Bedrock permissions to ECS task role:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"bedrock:InvokeModel",
"bedrock:InvokeModelWithResponseStream"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:bedrock:*::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-*",
"arn:aws:bedrock:*:*:inference-profile/*claude*"
]
}
]
}
- Ensure Bedrock is available in your region
- Check Service Control Policies (SCPs) aren’t blocking access
Solution:
- Update task role policy
- Check for SCPs (Service Control Policies) blocking access
- Verify cross-account permissions if using multiple accounts
Teams Integration Issues
Bot Shows as Offline
Causes & Solutions:
-
Azure Bot Channel Not Configured
- Azure Portal → Bot → Channels
- Ensure Teams channel is enabled
- Status should be “Running”
-
API Gateway Throttling
- Check CloudWatch metrics for 429 errors
-
Network Connectivity
- Verify security groups allow HTTPS outbound
- Check NAT Gateway is functioning (if used)
Issue: Bot responses show raw JSON or markdown
Solution:
- Update Teams app manifest version
- Ensure bot supports Adaptive Cards:
"supportsFiles": false,
"supportsCalling": false,
"supportsVideo": false
Bot Added but Can’t Use Commands
Issue: Bot visible but commands don’t work
Solution:
- Check bot is added to channel properly
- Verify @ mentions are working
- Test in personal chat first
- Check Teams app permissions
Google Chat Integration Issues
Bot Not Responding in Google Chat
Causes & Solutions:
-
Check Google Chat is Enabled
- CloudFormation parameter
GoogleChatEnabled must be true
- Verify ECS task has
GOOGLE_CHAT_ENABLED=true environment variable
-
Verify Webhook URL Configuration
- Go to Google Cloud Console → Chat API Configuration
- App URL must match CloudFormation output
GoogleChatWebhookURL
- Must end with
/api/google-chat
-
Check Service Account Credentials
- Verify
GoogleChatServiceAccountInfo parameter is correctly formatted
- JSON must be on a single line
- Project ID must match the service account’s project
“App Not Found” in Google Chat Search
Most Common Cause: Apps not published through Google Workspace Marketplace must explicitly list allowed users.
Solution:
-
Check Visibility Settings (most likely issue)
- Go to Google Cloud Console → APIs & Services → Google Chat API → Configuration
- Scroll to Visibility section
- Select “Make this Chat app available to specific people and groups”
- Click Add people or groups
- Add your email address explicitly (even if you’re the project owner)
- Click Save
- Wait 2-5 minutes for propagation
-
Verify Configuration is Saved
- Check for a green “Saved” confirmation
- Refresh the page and verify settings persisted
-
Try Different Discovery Methods
- In Google Chat: + New chat → Find apps → search for app name
- In a Space: Click space name → Apps & integrations → Add apps
Google Chat Authentication Errors
Symptoms: 401/403 errors in CloudWatch logs for /api/google-chat
Solution:
-
Check Lambda Authorizer Logs
- CloudWatch → Log Groups →
/aws/lambda/ohlala-gc-authorizer-{StackName}
- Look for specific error messages
-
Verify Audience URL
- In Chat API Configuration, Authentication Audience must be set to “App URL”
- The audience in JWT tokens will match your webhook endpoint
-
Validate Service Account JSON
- Ensure JSON is properly escaped when passed to CloudFormation
- Use
jq -c to convert to single line
Cards Not Rendering Properly in Google Chat
Issue: Charts or cards don’t display correctly
Solution:
-
Check QuickChart Container
- ECS task should have
quickchart container running
- Check container logs for errors
-
Verify S3 Bucket
- Chart images are stored in S3 bucket
smartops-charts-{StackName}
- Check bucket permissions and lifecycle rules
-
Check CloudWatch Logs
- Search for “chart” or “card” errors in main-bot logs
Google Chat vs Teams Behavior Differences
Known Differences:
- Message Updates: Google Chat has limited message update support
- Card Format: Uses Google Card JSON instead of Adaptive Cards
- Charts: Uploaded to S3 as images (Teams renders inline)
- @mentions: Required in spaces, optional in direct messages
Getting Support
-
Collect diagnostic information:
- Stack name and region
- Error messages (exact text)
- CloudWatch logs (last 100 lines)
- Time of occurrence
-
Try quick fixes:
- Restart ECS service
- Clear Teams cache
- Re-authenticate bot
Email: support@ohlala.cloud
Include:
- AWS Account ID
- Stack Name
- Error Description
- Steps to Reproduce
- Diagnostic Logs
Response Time: 1 business day
Additional Resources
6 - Deployment Reference
CloudFormation template parameters and advanced deployment configuration options
For step-by-step deployment, see the
Getting Started Guide. This page is for technical reference and customization.
Parameter Overview
The template supports two deployment modes:
- NewVPC: Creates complete network infrastructure (recommended)
- ExistingVPC: Integrates with your existing VPC
Required Parameters
Deployment Configuration
DeploymentMode
- Type: String
- Default:
NewVPC
- Allowed Values:
NewVPC, ExistingVPC
- Description: Choose to create a new VPC or use existing VPC infrastructure
ContainerImageTag
- Type: String
- Default:
v1.1.0
- Description: Container image tag version (e.g., v1.0.0, v1.1.0)
- Example:
v1.1.0
Microsoft Teams Configuration
MicrosoftAppId
- Type: String
- Description: Microsoft Teams Bot App ID
- Format: GUID format
- Example:
12345678-90ab-cdef-1234-567890abcdef
- Where to find: Azure Portal → Bot Resource → Configuration
- NoEcho: false
MicrosoftAppPassword
- Type: String
- Description: Microsoft Teams Bot App Password
- Format: String with special characters
- Example:
abcDEF123~hijKLM456-nopQRS789.tuvWXY012
- Where to find: Created during bot registration (save immediately!)
- NoEcho: true (hidden in console)
MicrosoftAppTenantId
- Type: String
- Description: Microsoft Teams Tenant ID
- Format: GUID format
- Example:
87654321-abcd-efgh-4321-0987654321fe
- Where to find: Azure Portal → Azure Active Directory → Overview
- NoEcho: false
Google Chat Configuration (Optional)
These parameters are optional and only needed if you want to enable Google Chat integration.
GoogleChatEnabled
- Type: String
- Default:
"false"
- Allowed Values:
"true", "false"
- Description: Enable Google Chat integration
- When to enable: If your organization uses Google Workspace and Google Chat
GoogleChatProjectId
- Type: String
- Default:
"" (empty)
- Description: Google Cloud Project ID for Google Chat integration
- Format: lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens
- Example:
my-company-smartops-123456
- Where to find: Google Cloud Console → Project selector → Project ID
- NoEcho: false
GoogleChatServiceAccountInfo
- Type: String
- Default:
"" (empty)
- Description: Google Chat service account JSON key (single line)
- Format: JSON string on a single line
- Where to find: GCP Console → IAM → Service Accounts → Keys → Create JSON key
- NoEcho: true (hidden in console)
- Important: Must be minified to a single line. Use
cat key.json | jq -c on Linux/Mac
AI Features (Optional)
EnableAIInsights
- Type: String
- Default:
"false"
- Allowed Values:
"true", "false"
- Description: Enable AI-powered insights in instance reports (uses Claude Sonnet 4 via Bedrock)
- When to enable: For enhanced analysis and recommendations in reports
Existing VPC Parameters
These parameters are required only when DeploymentMode: ExistingVPC:
ExistingVPCId
- Type: String
- Default:
"" (empty)
- Description: ID of existing VPC (e.g., vpc-12345678)
- Pattern:
^(vpc-[0-9a-f]{8,17})?$
- Example:
vpc-0123456789abcdef0
- Constraint: Must be a valid VPC ID or empty for NewVPC mode
ExistingPrivateSubnet1Id
- Type: String
- Default:
"" (empty)
- Description: ID of first private subnet (e.g., subnet-12345678)
- Pattern:
^(subnet-[0-9a-f]{8,17})?$
- Example:
subnet-0123456789abcdef0
- Requirement: Must be in different AZ from ExistingPrivateSubnet2Id
ExistingPrivateSubnet2Id
- Type: String
- Default:
"" (empty)
- Description: ID of second private subnet in different AZ (e.g., subnet-87654321)
- Pattern:
^(subnet-[0-9a-f]{8,17})?$
- Example:
subnet-0fedcba9876543210
- Requirement: Must be in different AZ from ExistingPrivateSubnet1Id
ExistingPublicSubnet1Id
- Type: String
- Default:
"" (empty)
- Description: ID of first public subnet (e.g., subnet-abcd1234)
- Pattern:
^(subnet-[0-9a-f]{8,17})?$
- Example:
subnet-0abcd1234efgh5678
- Requirement: Must be in different AZ from ExistingPublicSubnet2Id
ExistingPublicSubnet2Id
- Type: String
- Default:
"" (empty)
- Description: ID of second public subnet in different AZ (e.g., subnet-dcba4321)
- Pattern:
^(subnet-[0-9a-f]{8,17})?$
- Example:
subnet-0dcba4321hgfe8765
- Requirement: Must be in different AZ from ExistingPublicSubnet1Id
NewVPC Network Configuration
These parameters are optional and only used when DeploymentMode: NewVPC:
VPCCIDR
- Type: String
- Default:
10.0.0.0/16
- Description: CIDR block for the VPC
- Pattern: Valid IP CIDR range (x.x.x.x/x)
- Example:
10.0.0.0/16
PublicSubnet1CIDR
- Type: String
- Default:
10.0.1.0/24
- Description: CIDR block for public subnet 1
- Pattern: Valid IP CIDR range (x.x.x.x/x)
- Example:
10.0.1.0/24
PublicSubnet2CIDR
- Type: String
- Default:
10.0.2.0/24
- Description: CIDR block for public subnet 2
- Pattern: Valid IP CIDR range (x.x.x.x/x)
- Example:
10.0.2.0/24
PrivateSubnet1CIDR
- Type: String
- Default:
10.0.10.0/24
- Description: CIDR block for private subnet 1
- Pattern: Valid IP CIDR range (x.x.x.x/x)
- Example:
10.0.10.0/24
PrivateSubnet2CIDR
- Type: String
- Default:
10.0.11.0/24
- Description: CIDR block for private subnet 2
- Pattern: Valid IP CIDR range (x.x.x.x/x)
- Example:
10.0.11.0/24
EnableNATGateway
- Type: String
- Default:
"true"
- Allowed Values:
"true", "false"
- Description: Enable NAT Gateway for private subnets
- Cost Impact: NAT Gateway adds ~$32/month
- Recommendation: Set to
"false" for cost savings if outbound internet not needed
Stack Outputs
The template provides these outputs after successful deployment:
APIGatewayEndpoint
- Description: API Gateway endpoint URL
- Format:
https://{ApiGateway}.execute-api.{Region}.amazonaws.com/prod-{StackName}
- Usage: Base URL for API access
TeamsWebhookURL
- Description: URL to configure in Microsoft Teams Bot Framework
- Format:
https://{ApiGateway}.execute-api.{Region}.amazonaws.com/prod-{StackName}/api/messages
- Usage: Set this as the messaging endpoint in Azure Bot Configuration
GoogleChatWebhookURL
- Description: URL to configure in Google Chat API Configuration
- Format:
https://{ApiGateway}.execute-api.{Region}.amazonaws.com/prod-{StackName}/api/google-chat
- Usage: Set this as the App URL in Google Cloud Console → Chat API Configuration
ECSCluster
- Description: ECS Cluster Name
- Format:
OhlalaSmartOps-Cluster-{StackName}
- Usage: For monitoring and management
ECSService
- Description: ECS Service Name
- Format:
OhlalaSmartOps-Service-{StackName}
- Usage: For monitoring and scaling
VPCId
- Description: VPC ID (created or existing)
- Format:
vpc-xxxxxxxxx
- Usage: For reference and additional resource creation
Deployment Examples
Simple NewVPC Deployment
Parameters:
DeploymentMode: NewVPC
ContainerImageTag: v1.1.0
MicrosoftAppId: "12345678-90ab-cdef-1234-567890abcdef"
MicrosoftAppPassword: "your-secret-password"
MicrosoftAppTenantId: "87654321-abcd-efgh-4321-0987654321fe"
EnableNATGateway: "false" # Cost optimization
Custom NewVPC with Different CIDR
Parameters:
DeploymentMode: NewVPC
VPCCIDR: "172.16.0.0/16"
PublicSubnet1CIDR: "172.16.1.0/24"
PublicSubnet2CIDR: "172.16.2.0/24"
PrivateSubnet1CIDR: "172.16.10.0/24"
PrivateSubnet2CIDR: "172.16.11.0/24"
EnableNATGateway: "true"
# ... Teams parameters
ExistingVPC Deployment
Parameters:
DeploymentMode: ExistingVPC
ExistingVPCId: "vpc-0123456789abcdef0"
ExistingPrivateSubnet1Id: "subnet-0123456789abcdef0"
ExistingPrivateSubnet2Id: "subnet-0fedcba9876543210"
ExistingPublicSubnet1Id: "subnet-0abcd1234efgh5678"
ExistingPublicSubnet2Id: "subnet-0dcba4321hgfe8765"
# ... Teams parameters
Parameter Validation
The template includes validation rules:
Pattern Validation
- VPC IDs: Must match
vpc- followed by 8-17 hex characters
- Subnet IDs: Must match
subnet- followed by 8-17 hex characters
- CIDR Blocks: Must be valid IP CIDR format
Logical Validation
- ExistingVPC mode requires all four subnet IDs
- Subnets must be in at least 2 different availability zones
- CIDR blocks must not overlap
Cross-Parameter Rules
- If
DeploymentMode: ExistingVPC, all existing VPC parameters are required
- If
DeploymentMode: NewVPC, existing VPC parameters are ignored
Cost Impact by Parameter
| Parameter |
Cost Impact |
Notes |
EnableNATGateway: "true" |
+$32/month |
Only for NewVPC mode |
EnableNATGateway: "false" |
$0 |
Saves money but no outbound internet |
DeploymentMode: ExistingVPC |
$0 |
Uses existing network infrastructure |
ContainerImageTag |
$0 |
No cost difference between versions |
Common Parameter Errors
Missing Required Parameters
Template validation error: Parameter 'MicrosoftAppId' must have a value
Solution: Provide all required Teams configuration parameters
Parameter validation failed: vpc-invalid does not match pattern
Solution: Use correct format: vpc- + 8-17 hex characters
Subnet AZ Requirements Not Met
The subnet IDs must be in at least two different availability zones
Solution: Choose subnets from different AZs in your region
ExistingVPC Missing Parameters
When using ExistingVPC mode, you must provide all subnet IDs
Solution: Provide all four subnet parameters for ExistingVPC mode
Additional Resources

















































